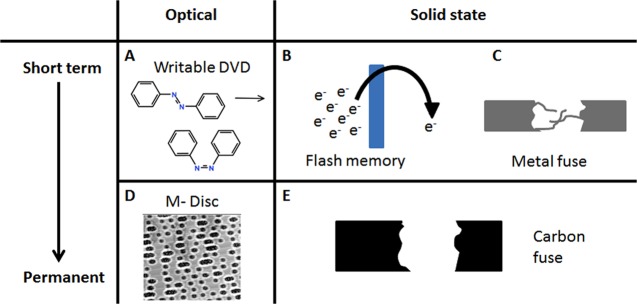
Figure 1.
Concept diagram of materials for data storage, from short term to permanent, relating materials that have been used for data storage and their permanence. (A) Optical disks can undergo chemical changes, resulting in a change of optical properties. (B) In integrated circuits, tunneling and electromigration can cause data instability. (C) Metal fuses suffer from thermal movement of atoms, resulting in the formation of dendrites. (D) M-disk is the structurally based permanent data-storage device that is currently available. (E) Carbon nanofuses use a structural mechanism to store the data; however, unlike metal fuses, the carbon is stable due to its high local bond strength.