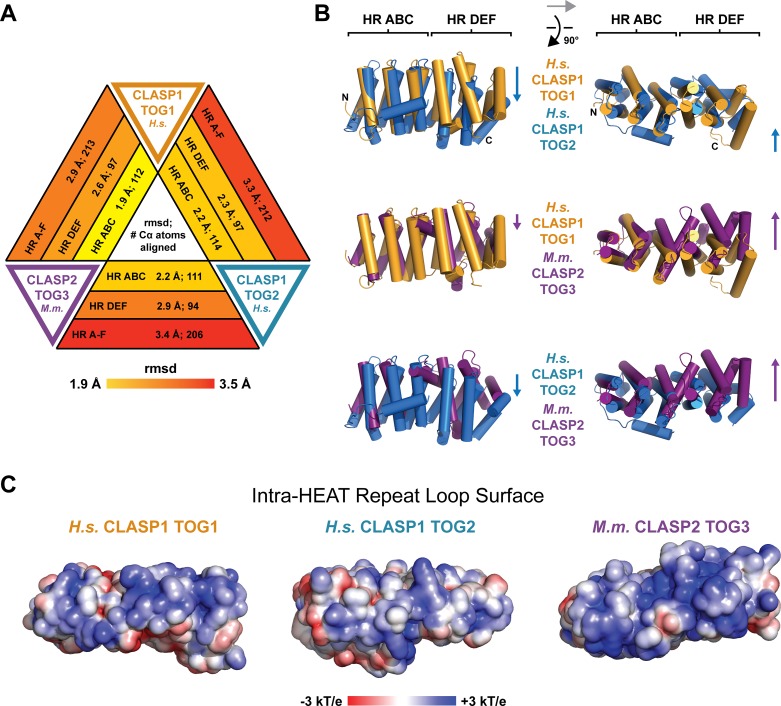
Fig 5. CLASP family TOG1, TOG2, and TOG3 domains each have unique architectures.
(A) Comparison of H.s. CLASP1 TOG1, H.s. CLASP1 TOG2, and M.m. CLASP2 TOG3 (PDB accession code 3WOZ, [44]) structures using rmsd analysis of corresponding Cα atoms across the three domains (Table 2, Dali server [52]). Pairwise analysis was performed, comparing HRs A-C, D-F, and all six HRs: A-F. (B) Pairwise structural comparison of CLASP family TOGs 1–3. The H.s. CLASP1 TOG2 and M.m. CLASP2 TOG3 HR A-C triad was structurally aligned to the H.s. CLASP1 TOG1 HR A-C triad using the Dali server and respective pairwise comparisons generated [52]. Images at left are oriented with each domain’s intra-HR loops positioned at the top of the domain as shown. The images at right were produced after a 90° rotation about the x-axis and focus on the respective surfaces composed of intra-HR loops. (C) Electrostatic surface potential mapped on the structures of H.s. CLASP1 TOG1, H.s. CLASP 1 TOG2, and M.m. CLASP2 TOG3. The surface of each domain presented is the surface composed of intra-HR loops, oriented as presented in the images at right in panel B.