FIG. 1.
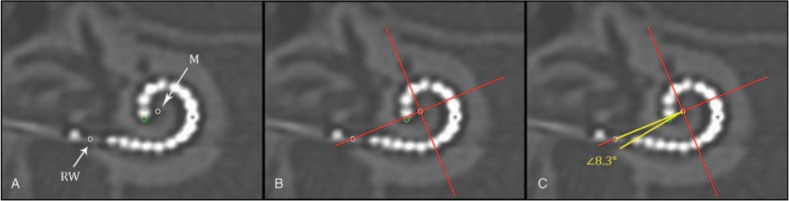
Method for angular insertion depth measurement on Computed Tomography (CT)-scan of an implanted electrode array with 16 electrode contacts. With in a three-dimensional cylindrical coordinate system all spatial information of the cochlea and an implant is measurable. By consensus this cochlear framework is defined by a plane of rotation through the basal turn of the cochlea and a z-axis through the modiolus. This can be applied on CT of the temporal bone by making a multiplanar reconstruction along the basal turn of the cochlea (A–C), and placing the z-axis through the center of the cochlea; the modiolus (M). A, An angular measurement of the insertion depth can then be made by indicating the center of the round window (RW) and the tip of the electrode array (dark grey circle). B, A 0 degree reference line between the modiolus (M) and the middle of the round window (RW), and a perpendicular line from the modiolus on the 0 degree reference line is drawn (cross). C, An angle is drawn (in white) from the modiolus over the 0 degree reference line, and through the most apical point the tip of the electrode array (dark grey circle). In this example the angular insertion depth of the most apical electrode contact is 368.3 degrees; the sum of four quadrants equal to 360 degrees plus the measured white angle equal to 8.3 degrees.
