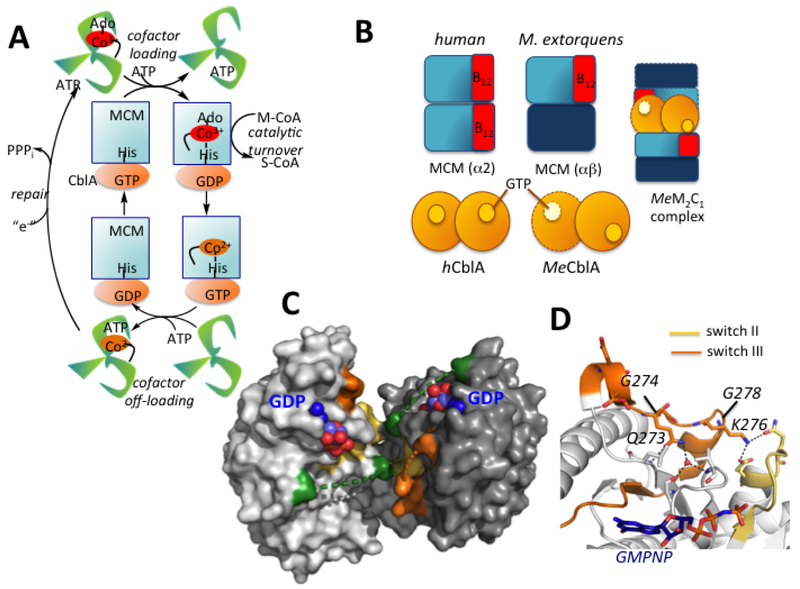
Figure 1. Chaperone functions and structure of human CblA.
(A) AdoCbl is loaded onto MCM from ATR in a process gated by the GTPase activity of CblA. MCM has GAP function and enhances the GTPase activity of CblA when the two proteins form a complex. Holo- MCM catalyzes the isomerization of methylmalonyl-CoA (M-CoA) to succinyl-CoA (S-CoA). When MCM is inactivated, the GTPase activity of CblA is used to off-load cob(II)alamin to the ATR active site. ATR completes the repairs process, reforming AdoCbl. (B) Cartoon showing differences between human and M. extorquens MCM and CblA and the M extorquens M2C1 complex that was previously characterized. (C) Structure of human CblA (PDB: 2WWW) with GDP bound. Switch I (green), II (yellow) and III (orange) loops are highlighted. Dashed lines represent disordered regions in switch I and III loops. (D) Since switch III residues 268–274 in human CblA are disordered, a close-up of the homologous region in MeMeaB (PDB: 4YJB) is shown with the location of residues (human numbering) mutated in this study.