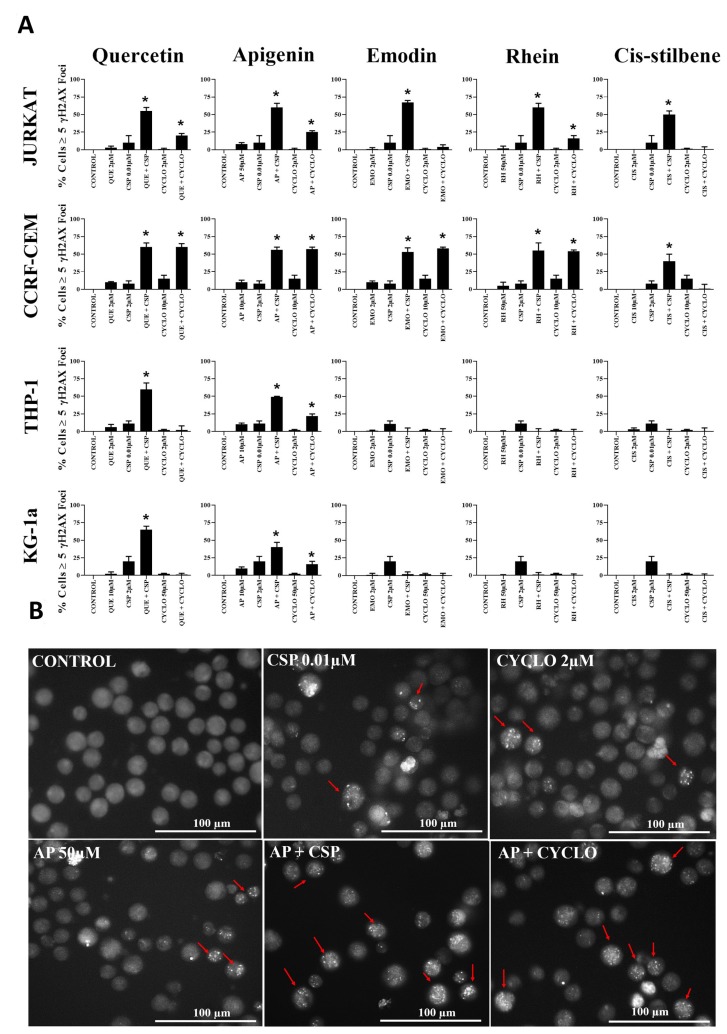
Figure 6.
(A) The effect of two alkylating agents: cisplatin (CSP) and cyclophosphamide (CYCLO) on γ-H2AX foci formation (DNA damage marker) when used in combination with quercetin (QUE), apigenin (AP), emodin (EMO), rhein (RH) or cis-stilbene (CIS); in two lymphoid (Jurkat and CCRF-CEM) and two myeloid (THP-1 and KG-1a) leukaemia cell lines. This was evaluated by the immunofluorescent staining using Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-H2AX (pS139). Cells were treated with CSP, CYCLO or CLB and polyphenols alone and in combination for 24 h using their lowest-significant doses (LSD). The data was expressed as medians and ranges (N = 4). Data was normalised to the vehicle control which was assigned 0% of γ-H2AX foci formation (DNA damage marker). Effects of combination treatments were statistically classified as synergistic (*) causing an increase in the percentage of cells with γ-H2AX foci or antagonistic (#) causing a decrease in the percentage of cells with γ-H2AX foci; when compared to vehicle control, drugs alone and expected values of combination treatments. Statistical significant was set at P ≤ 0.05. (B) An example of immunofluorescent detection of DNA damage (measured as γ-H2AX foci) for Jurkat lymphoid leukaemia cells when treated with LSDs of cisplatin (CSP) and cyclophosphamide (CYCLO) alone and in combination with apigenin (AP) for 24 h. Cells with ≥5 foci (red arrows) are identified as having DNA damage. Images were captured in bright filed using (Cell-F software, Olympus). Scale bar = 100 μm.