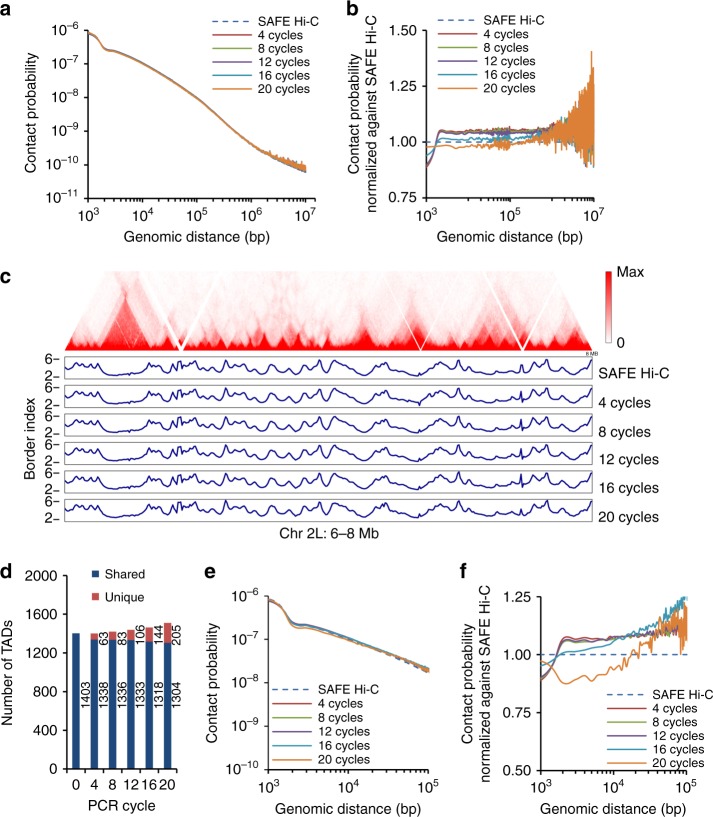
Fig. 3.
Distance-related amplification bias and topologically associated domain (TAD) identification in Drosophila genome. a Chromatin interaction frequency as a function of genomic distance averaged across the Drosophila genome. b Average chromatin interaction frequency across the genome normalized against SAFE (simplified, amplification-free, and economically efficient process) Hi-C for the Drosophila genome. c Hi-C interaction heatmap for the region of chromosome 2 L from 6 to 8 Mb is shown. Fluctuation pattern of border index is shown below heatmap for SAFE Hi-C and amplified Hi-C. d Dark blue bars show the number of TADs shared with SAFE Hi-C; red bars show the number of TADs uniquely found for amplified Hi-C libraries. e Chromatin interaction frequency averaged within the TADs was plotted as a function of genomic distance. f Average chromatin interaction frequency within the TADs was normalized against SAFE Hi-C