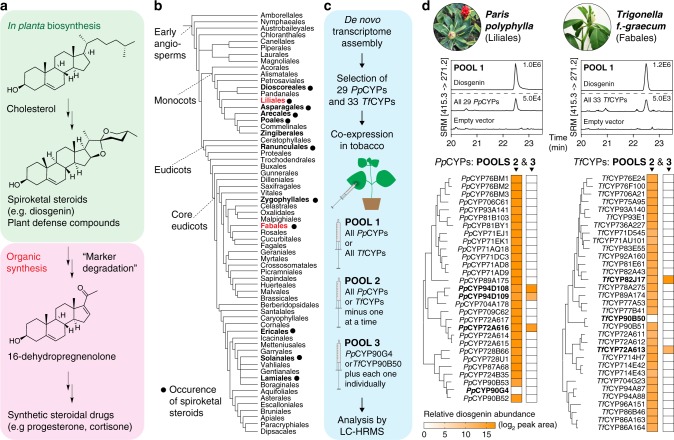
Fig. 1.
Identification of diosgenin-biosynthetic cytochrome P450s using pooled-screen approach. a Diosgenin is biosynthetically derived from cholesterol, and used as the precursor for the synthetic production of steroidal drugs via “Marker degradation”14. b Phylogenetic relationship of plant families that reportedly harbor spiroketal steroid chemotypes. P. polyphylla and the T. fenum–graecum, belonging to Liliales and Fabales respectively, are the two species investigated in this study. Angiosperm phylogeny was obtained from Theodor C.H. Cole, Hartmut H. Hilger, and Peter F. Stevens. c The stepwise pooled-screen approach employed in this study to identity diosgenin-biosynthetic CYPs from P. polyphylla and T. fenum–graecum. The screens were conducted using the combinatorial transient gene expression system in Nicotiana benthamiana. d Identification of the diosgenin-biosynthetic CYPs from P. polyphylla and T. fenum–graecum. 29 CYPs from P. polyphylla (PpCYPs) and 33 CYPs from T. foenum–graecum (TfCYPs) were selected for the screens. In the initial screen (POOL 1), co-expression of all PpCYPs or all TfCYPs resulted in diosgenin accumulation in N. benthamiana, shown in selected reaction monitoring chromatograms (SRM) from LC–MS data (peak intensity is indicated). In the second step (POOL 2), batches of CYPs omitting one CYP at a time were tested. PpCYP90G4 and TfCYP90B50 were identified as essential for reconstituting diosgenin production in N. benthamiana. In POOL 3, each PpCYP or TfCYP was co-expressed with PpCYP90G4 or TfCYP90B50, respectively. Three PpCYPs (PpCYP94D108, PpCYP94D109, and PpCYP72A616) and two TfCYPs (TfCYP82J17 and TfCYP72A613) were identified as capable of completing diosgenin biosynthesis together with PpCYP90G4 or TfCYP90B50. CYP candidates are organized based on their maximum-likelihood phylogenetic relationship. The relative abundance of diosgenin accumulation in transgenic N. benthamiana is shown as heat map