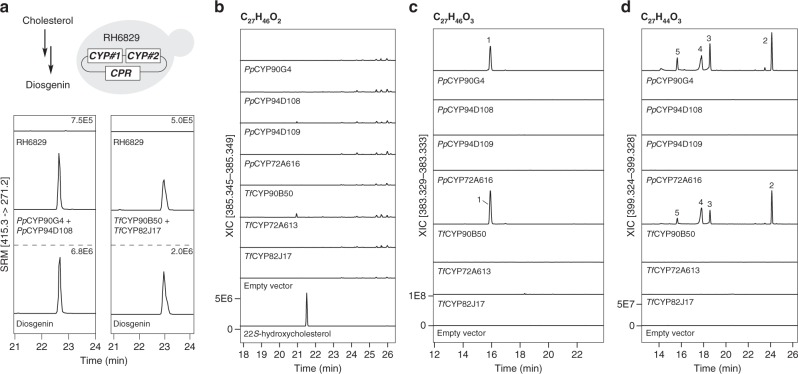
Fig. 2.
Elucidation of CYP-mediated diosgenin biosynthesis from cholesterol. a Reconstitution of diosgenin biosynthesis in the yeast strain RH6829, which was engineered to accumulate cholesterol25. Co-expression of CYP pairs PpCYP90G4/PpCYP94D108 or TfCYP90B50/TfCYP82J17 together with a CYP reductase (CPR) from A. thaliana (ATR1) led to diosgenin production in RH6829 yeast, shown in selected reaction monitoring chromatograms (SRM) from LC–MS data (peak intensity is indicated). b–d LC-HRMS-based metabolic profiling of transgenic N. benthamiana expressing individual diosgenin-biosynthetic CYPs from P. polyphylla and T. foenum–graecum. Extracted ion chromatograms (XICs) corresponding to putative monohydroxylated cholesterol with predicted molecular formula of C27H46O2 (identified as [M + H-H2O]+ ions) b, and putative dihydroxylated-cholesterol derivatives C27H46O3 (identified as [M + H-2H2O]+) c and C27H44O3 (identified as [M + H-H2O]+ ions) d are displayed. Major products detected in N. benthamiana expressing PpCYP90G4 or TfCYP90B50 are labeled as compounds 1–5