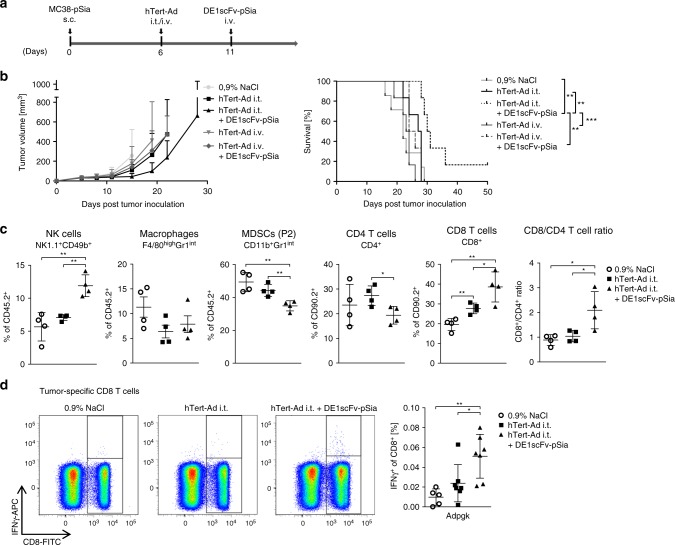
Fig. 5.
Ab-retargeting after intratumor application of an oncolytic adenovirus leads to improved survival. a Subcutaneous MC38-pSia tumors were established in Ad5-naive mice. After tumor formation, animals received a single application of the oncolytic adenovirus hTert-Ad (by either intratumor or intravenous application) followed by a single i.v. administration of DE1scFv-pSia as shown in the treatment scheme. Control animals were treated by i.t. injection of saline. b Tumor development and survival were monitored (group size n = 6, except control group 0.9 % NaCl: n = 7, median survival: 0.9% NaCl 22 days; hTert-Ad i.v. 23.5 days; hTert-Ad i.t. 27.5 days; hTert-Ad i.v. + DE1scFv-pSia 25 days; hTert-Ad i.t. + DE1scFv-pSia 30.5 days). c Tumor-infiltrating immune cells were analyzed on day 8 after start of i.t. virotherapy (n = 4 in all groups). Proportions of NK cells, macrophages, and MDCSs were calculated as percentage of CD45.2-positive tumor-infiltrating leukocytes. CD8 and CD4 T-cell frequencies were calculated as percentage of CD90.2-positive lymphocytes. d Analyses of tumor antigen-specific CD8 T cells in splenocytes 13 days after i.t. virotherapy (0.9% NaCl: n = 5; hTert-Ad: n = 7; hTert-Ad + DE1scFv-pSia: n = 7). To determine neoantigen-specific responses against Adpgk-R304M, splenocytes were stimulated with the peptide ASMTNMELM, or an irrelevant control peptide, and were analyzed by intracellular staining of IFNγ and flow cytometry. Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test was used to calculate survival statistics in b. Two-tailed unpaired t test was used to calculate statistics in c and d. *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001. Error bars refer to standard deviation (SD). Source data are provided as a source data file