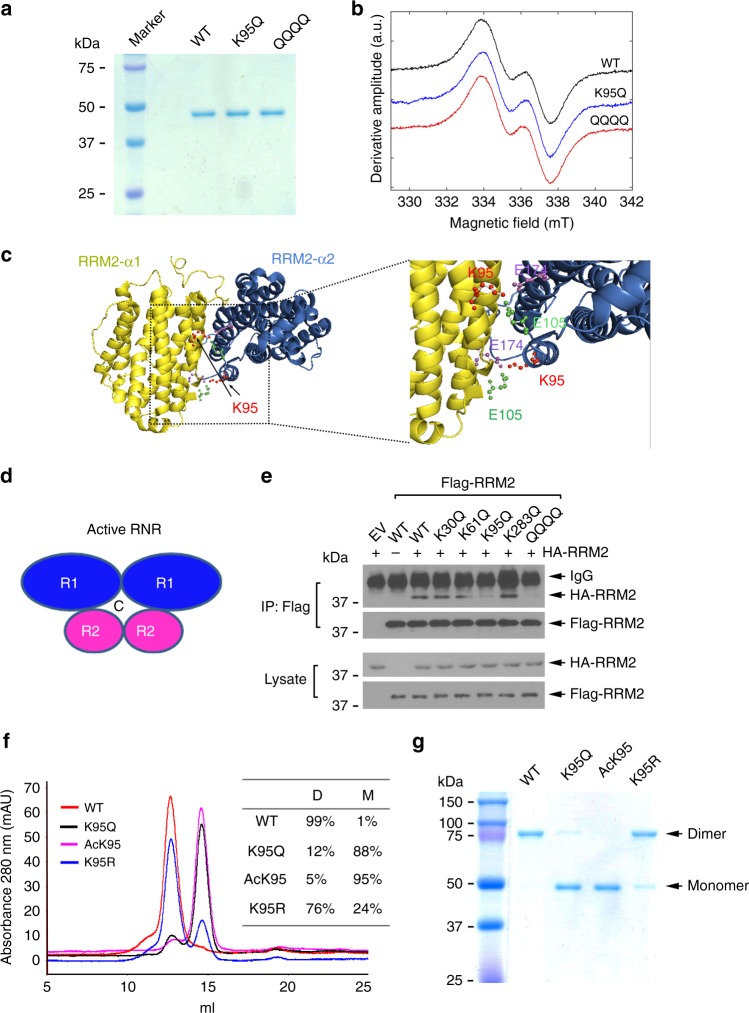
Fig. 2.
RRM2 acetylation at K95 disrupts its homodimerization. a Recombinant His-tagged WT, K95Q, and QQQQ RRM2 proteins were purified from E. Coli. b Tyrosyl radical concentrations were measured by EPR spectroscopy: EPR spectra of WT, K95Q, and QQQQ RRM2 proteins. c K95 location within RRM2 structure (left panel). The RRM2 homodimer structure (PDB ID: 3OLJ) is shown, and K95 is predicted to form a salt bridge with E105 and E174 (right panel). d Schematic of active RNR complex. e H1299 cells were co-transfected with HA-RRM2 and Flag-tagged acetyl-mimetic RRM2 mutants, followed by co-IP using a Flag antibody. HA-RRM2 and Flag-RRM2 were analyzed by western blot using anti-HA or anti-Flag antibody, respectively. f Dimerization of recombinant WT, K95Q, AcK95, and K95R RRM2 proteins was analyzed by gel filtration chromatography. g SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant WT, K95Q, AcK95, and K95R RRM2 proteins after cross-linking with 2 mM disuccinimidylsuberate