Fig. 7.
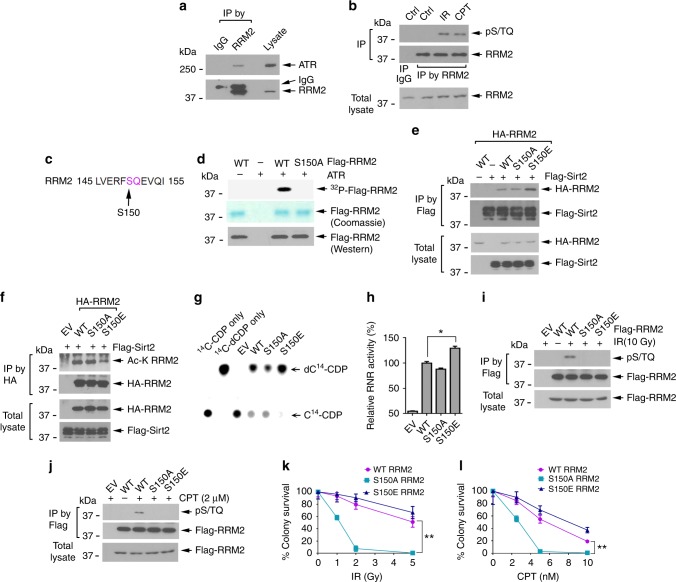
ATR phosphorylation of RRM2 facilitates its deacetylation in response to DNA damage. a Co-IP in H1299 cells using RRM2 antibody. IgG was used as a IP control. RRM2-associated ATR was analyzed by western blot. b H1299 cells were exposed to IR (10 Gy) or treated with CPT (2 µM) for 6 h, followed by IP using RRM2 antibody. Phosphorylation of RRM2 was analyzed by western blot using phospho-S/TQ motif-specific (pS/TQ) antibody. c ATR phosphorylation motif “SQ” in human RRM2 protein. d Active ATR kinase was immunoprecipitated from H1299 cells treated with IR (10 Gy) and incubated with purified Flag-tagged WT or S150A mutant RRM2 protein in kinase buffer containing [γ-32P] ATP. RRM2 phosphorylation was analyzed by autoradiography. e, f RRM2 phosphorylation at S150 enhances its interaction with Sirt2. Flag-tagged Sirt2 was co-transfected with HA-tagged WT, S150A, or S150E RRM2 into H1299 cells, followed by analysis of HA-RRM2/Flag-Sirt2 binding and acetylation of HA-RRM2. g, h Flag-tagged WT, S150A, or S150E RRM2 mutant protein was immunoprecipitated from H1299 cells overexpressing exogenous Flag-tagged WT, S150A, or S150E, then mixed with 1 µg of purified GST-RRM1 protein, followed by TLC analysis for RNR activity. The error bars indicate ± s.d. of three separate experiments. *P<0.05, by two-tailed t test. i, j H1299 cells overexpressing exogenous Flag-tagged WT, S150A, or S150E mutant RRM2 were treated with IR (10 Gy) or CPT (2 µM), followed by analysis of phosphorylation of Flag-RRM2. k, l Endogenous RRM2 was depleted from H1299 cells using 3′-UTR targeted RRM2 shRNA. HA-tagged WT, S150A, or S150E was transfected in H1299 RRM2-deficient cells using pBabe retroviral construct. Cells were treated with IR or CPT, followed by colony-formation analysis. The error bars indicate ± s.d. of three separate experiments. **P < 0.01, by two-tailed t test