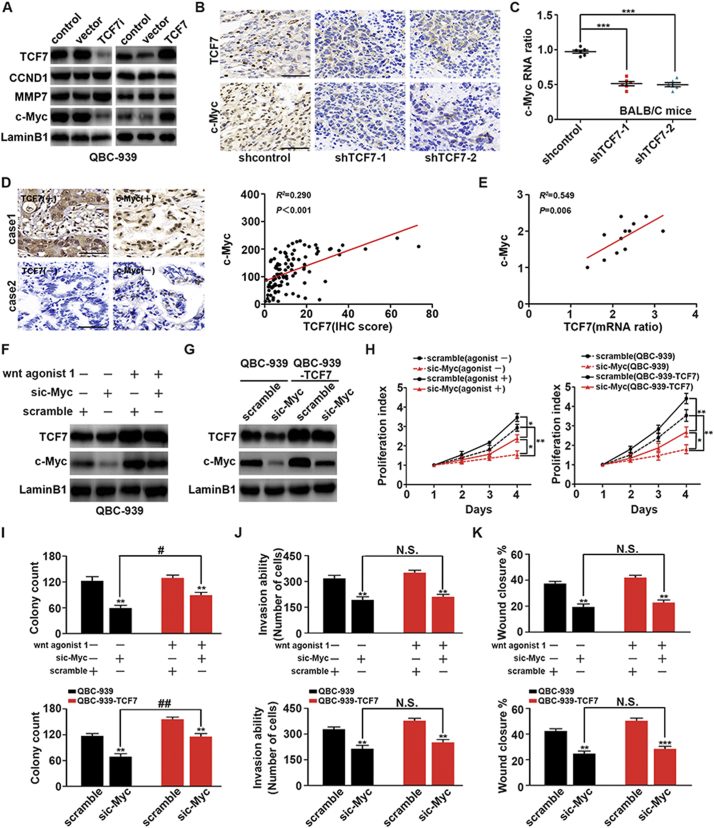
Fig. 3.
c-Myc was required for TCF7-induced proliferation, migration, and invasion. (A) After silencing or overexpressing TCF7 in QBC939 cells, expression levels of c-Myc, CCND1, and MMP7 were detected by western blotting. (B) Representative c-Myc IHC staining in xenograft tumors with transfection of empty vector or shTCF7. Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) mRNA level of c-Myc in control xenografts and xenografts with TCF7 knockdown. (D) Correlation of IHC scores for TCF7 and c-Myc in PHCC tissues. (E) Association of c-Myc mRNA levels with TCF7 levels in eight fresh human PHCCs. (F) Effects of Wnt agonist 1 (20 μM, 8 h) on TCF7 and c-Myc expression in QBC939 cells. (G) Expression of c-Myc was knocked down in normal QBC939 cells or QBC939 cells overexpressing TCF7. (H) CCK8 assays showing the effects of c-Myc silencing and Wnt agonist 1 on proliferation in QBC939 cells. * and ** represent P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively, between the indicated subgroups. (I) Effects of TCF7 knockdown, TCF7 overexpression, and c-Myc knockdown on colony formation ability in QBC939 cells. (J and K) Effects of c-Myc knockdown with TCF7 overexpression or Wnt agonist 1 stimulation on soft agar transwell assays (J) and wound healing assays (K) in QBC939 cells. *, **, and *** indicate P < 0.05, P < 0.01, and P < 0.001, respectively, compared with the corresponding control groups. ## represents P < 0.01 between the indicated groups. Analyzed data were from at least three independent experiments.