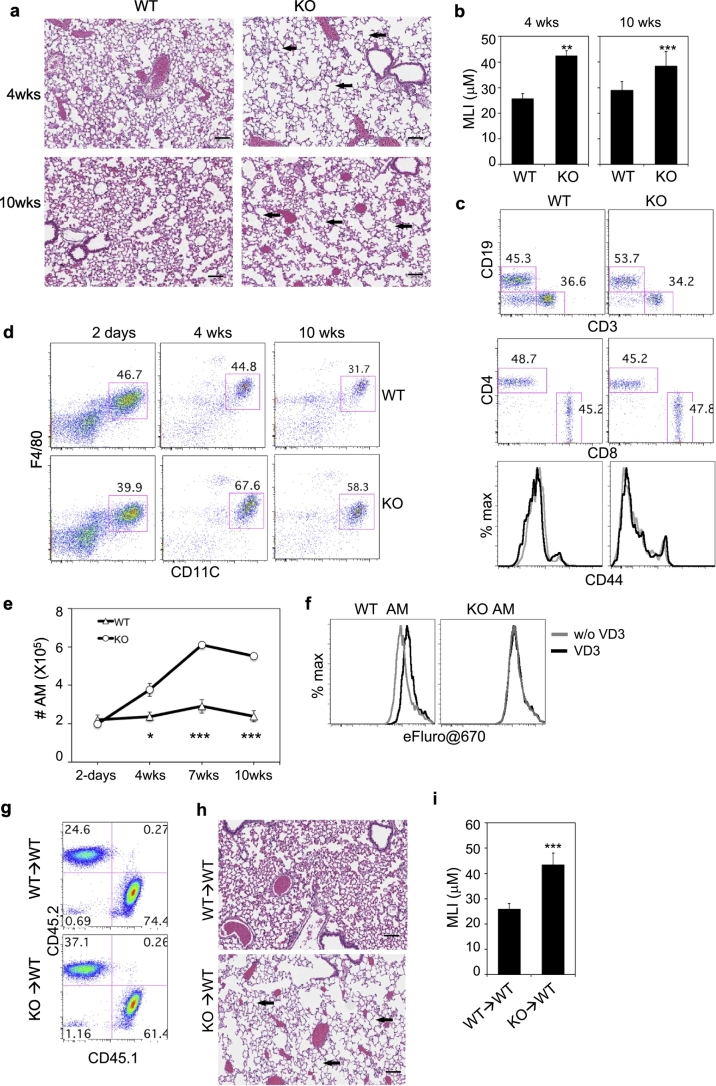
Fig. 4.
Accumulation of AM and development of emphysema in Vdr−/− mice. a, Comparison of H&E staining of lung sections from 4- and 10-weeks old wildtype (WT) and Vdr−/− littermates. b, Quantification of mean linear intercept (MLI) of alveolar airspace in WT and Vdr−/− littermates. n = 3 per genotype and age group. c, Flow cytometry analysis of T and B cells from the lung tissues of WT and Vdr−/− littermates at 4 weeks of age. Single cell suspension was prepared by digesting the lung tissue and stained for CD45, CD19, CD3, CD4, CD8, NK1.1 and CD44. Shown are representative CD19 versus CD3 staining profiles gating on CD45+ cells, CD4 versus CD8 staining profiles gating on CD3+ cells. Histograms show CD44 expression by CD4 T cells (left) and CD8 T cells (right) from WT (black) and Vdr−/− (grey) mice. The results from the same staining of 10-week-old WT and Vdr−/− mice are shown in Fig. S6a. d, Cells from BAL were stained for CD45, F4/80, CD11c, CD11b, MHCII and SiglecF. Shown are representative CD11c versus F4/80 staining profiles of CD45+ cells from WT and Vdr−/− littermates at different ages. Expression of F4/80, MHCII, CD11b, CD11c and SiglecF by AM are shown in Fig. S6b. e, Comparison of AM numbers in the BAL of WT and Vdr−/− mice at different ages (n = 6 mice each per genotype and age group). f, Inhibition of GM-CSF-induced AM proliferation by VD3. WT and Vdr−/− AM were labeled with eFluor®670 and cultured in the presence of GM-CSF for two days with or without VD3. Shown are representative eFluor®670 histograms from one of the three experiments. A decrease in eFluor®670 intensity indicates cell proliferation. g-i, Induction of pulmonary emphysema by intratracheal transfer of Vdr−/− AM into WT B6 mice. 5 × 105 WT or Vdr−/− AM (CD45.2+) were adoptively transferred into CD45.1+ B6 recipient mice every week for four weeks (n = 4 per group). At the 6th week, recipient mice were euthanized for flow cytometry to confirm the presence of the transferred cells in BAL (g) or H&E staining of lung sections (h) to quantify the mean linear intercept (MLI) of alveolar airspace (i). Scale bars in a and h: 100 μm. The numbers in c, d and g indicate percentages of cells in the gated regions. The arrows in a and h indicate enlarged alveolar space. Error bars indicate standard deviation (SD). P value was calculated by t-test. * P < .05, ** P < .01, *** P < .001.