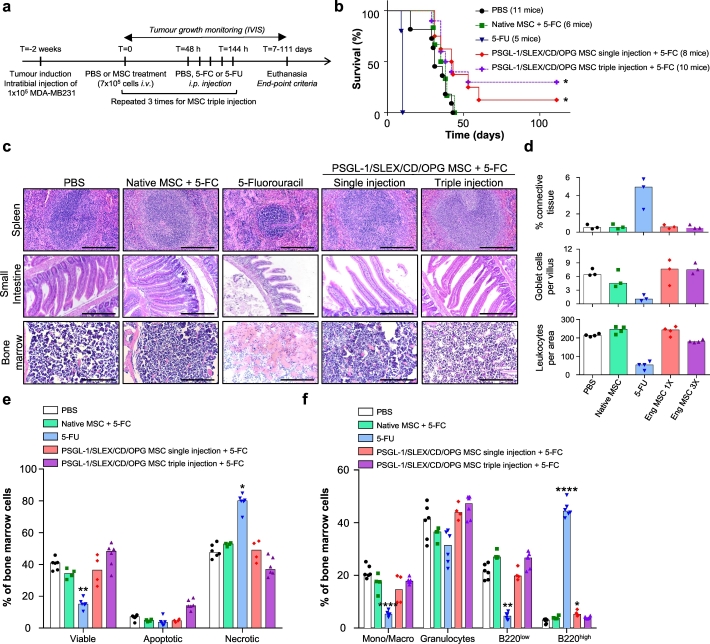
Fig. 6.
Systemic infusion of PSGL-1/SLEX/CD/OPG MSC improves animal survival without inducing systemic toxicity in the MDA-MB231 intratibial model.
(a) Timeline of the therapeutic treatments. PBS or 7 × 105 MSC (Native or PSGL-1/SLEX/CD/OPG) were injected i.v. and 48 h later 500 mg/kg 5-FC or 200 mg/kg 5-FU was injected i.p. once a day for 5 days. Mice were euthanised as defined by end-point criteria (total photon flux >1010 p/s, signs of pain or distress, etc.). (b) PSGL-1/SLEX/CD/OPG MSC treatment improves overall animal survival. The graph shows the percentage of survival of the animals in the different groups: CT (PBS control, 11 mice), Native MSC + 5-FC treatment (6 mice), 5-FU (5 mice), PSGL-1/SLEX/CD/OPG MSC single injection +5-FC treatment (8 mice) and PSGL-1/SLEX/CD/OPG MSC triple injection +5-FC treatment (10 mice). Statistical analysis: Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test, * p ≤ .05. (c) PSGL-1/SLEX/CD/OPG MSC treatment group exhibits minimal systemic toxicity compared to 5-FU treatment. Tissue analysis was performed following H&E staining to evaluate toxicity-induced damage. Panel shows organs where the greatest damage was observed: spleen, small intestine, and bone marrow. Scale bars: 500 μm for spleen and bone marrow, 250 μm for the small intestine. (d) Engineered MSC did not induce significant tissue damage. Quantifications were done on the H&E staining: percentage of connective tissue to assess spleen fibrosis, number of goblet cells per villus to evaluate intestine damage, and number of leukocytes per bone marrow area to measure toxicity. Bar graph shows the median for each group, and each point represents one animal, n = 4 mice per group. Eng MSC = PSGL-1/SLEX/CD/OPG MSC. (e) Engineered MSC did not lead to significant cell death in the bone marrow. Flow cytometry was performed on bone marrow to analyse the percentages of viable, apoptotic and necrotic cells. 2 to 3 animals were used for each group, and both legs were analysed. As no major differences were observed between the healthy and the tumour leg, data from both legs were pooled. Bar graph shows the median for each group, and each point represents one analysed leg. Statistical analysis: Kruskal-Wallis followed by a Dunn's multiple comparison test among each group (viable, apoptotic and necrotic) to compare all conditions to the control; * p ≤ .05, ** p ≤ .01. (f) Engineered MSC did not significantly alter cell composition of the bone marrow. Flow cytometry was performed on equal numbers of bone marrow cells to analyse the different populations: monocytes/macrophages (Mono/Macro), granulocytes and B lymphocytes (B220low and B220high). 2 to 3 animals were used for each group, and both legs were analysed. As no major differences were observed between the healthy and the tumour leg, data from both legs were pooled. Bar graph shows the median for each group, and each point represents one analysed leg. Statistical analysis: Kruskal-Wallis followed by a Dunn's multiple comparison test among each population to compare all conditions to the control; * p ≤ .05, **** p ≤ .0001.