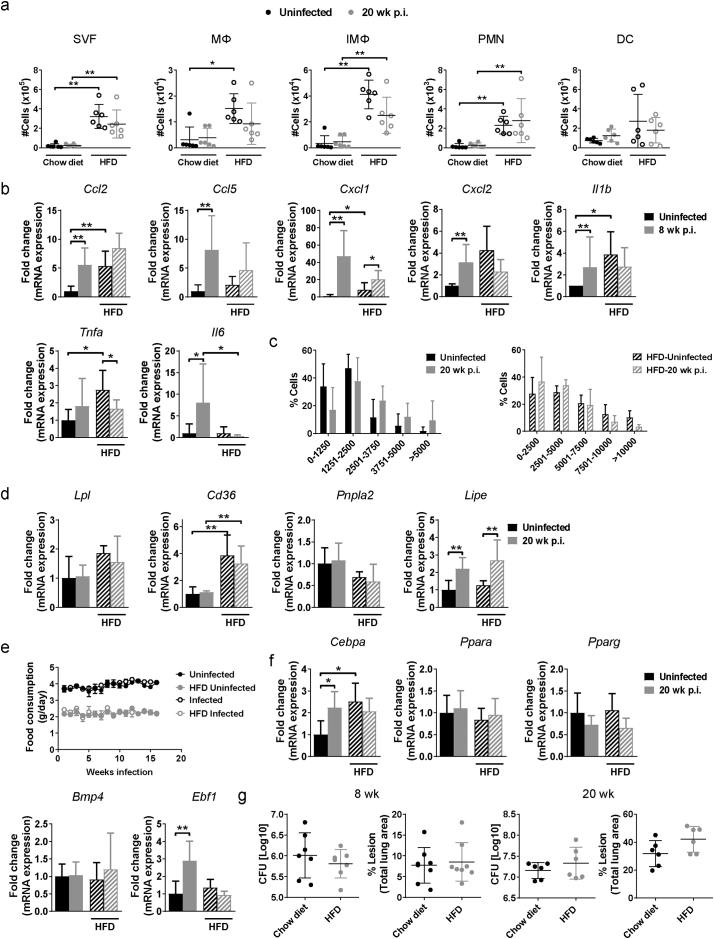
Supplementary Fig. S6.
Modulation of adipose tissue inflammation, lipid metabolism and adipogenesis in mice on a HFD by M. tuberculosis. (a) Number of stromal vascular cells (SVF), macrophages (MΦ), inflammatory macrophages (IMΦ), polymorphonuclear cells (PMN) and dendritic cells (DC)in perigonadal white adipose tissue (pgWAT) from uninfected mice or mice infected for 20 wk. and were fed chow or HFD. (b) Gene expression of Ccl2, Ccl5, Cxcl1, Cxcl2, Il1b, Tnf1, and Il6 in pgWAT 8 wk. p.i. (c) Adipocyte size in uninfected mice or mice infected for 20 wk. and were fed chow or HFD. (d) Gene expression of Ldl, Cd36, Pnpla2, and Lipe in pgWAT from uninfected mice or 20 wk. after infection on a chow or HFD. (e) Food consumption in uninfected mice or mice infected for 20 wk. and were fed chow or HFD. (f) Gene expression of Cebpa, Ppara, Pparg, Bmp4 and Ebf1 20 wk. p.i. (g) Lung bacterial burden and percentage of lung lesion in mice on a chow diet or HFD that were infected for 8 wk. (left panels) or 20 wk. (right panels). Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6–8). All the experiments were repeated at least twice. *P < 0·05 and **P < 0·01.