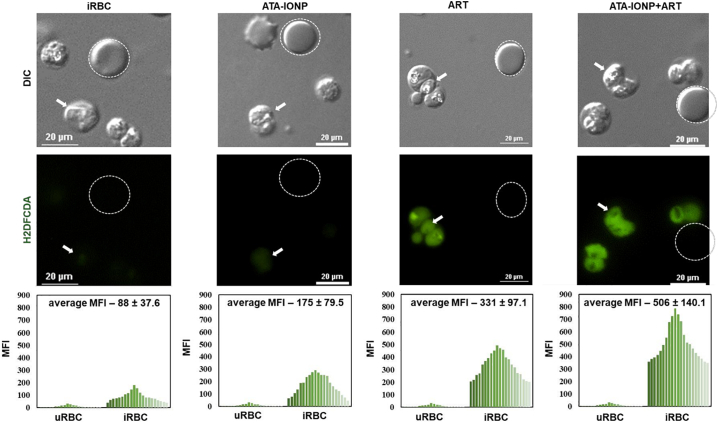
Fig. 7.
Iron oxide nanoparticle combination maximizes oxidative stress level in P. falciparum parasite.
Increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) level was monitored by H2DCFDA assay. Plasmodium-infected RBCs with 3% parasitemia were treated with or without 100μg/mL ATA-IONPs in the presence and absence of ART (2 nM) for 3 h. Prior to nanoparticle and drug treatment, infected RBCs were pretreated with 20 μM DCFDA for 30 min. Images were captured in Nikon Ti2 eclipse fluorescent microscopy (magnification 100×). The graphical representation shows mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) for DCFDA fluorescence between uninfected and infected RBCs for each set of treatment. An enhanced fluorescence signal in ART-treated cells in the presence of iron oxide nanoparticle is observed in comparison with that of ART alone. The difference between the MFI of ART and ATA-IONP+ART is statistically analyzed by students t-test and was found to be significant (p-value 0.017).