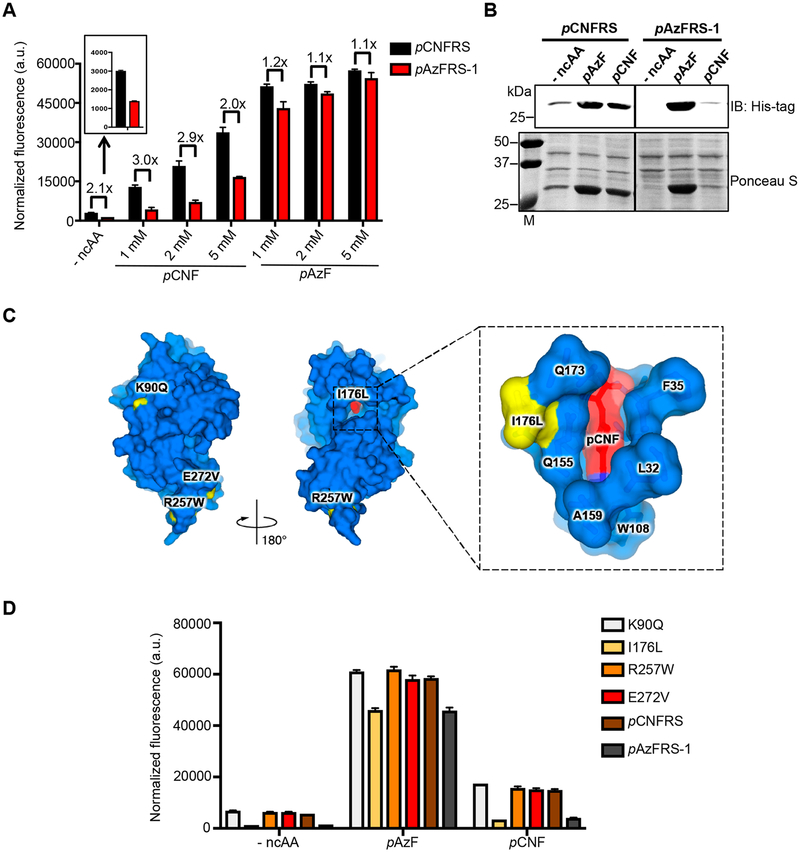
Figure 2.
Directed evolution of pAzF-selective aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. (A) The variant pAzFRS-1 has reduced misincorporation levels of canonical amino acids and is more selective for pAzF than parental enzyme pCNFRS. Cells expressing pCNFRS or pAzFRS-1 with its cognate tRNACUATyr and sfGFP-2TAG were grown in LB media containing varying concentrations of indicated ncAAs. Incorporation efficiencies were evaluated by monitoring sfGFP fluorescence. Normalized fluorescence intensities were calculated from fluorescence readings at 24 h time points divided by absorbance at 600 nm. Mean values and standard deviations were calculated from three replicates. (B) Western blotting with anti-His6 tag for full-length sfGFP (top), Ponceau S staining of membrane (bottom). Cells expressing pCNFRS or pAzFRS-1 with its cognate tRNACUATyr and sfGFP-2TAG were grown in LB media containing the indicated ncAAs (1 mM). (C) Four amino acid substitutions (K90Q, I176L, R257W, E272V) were found in pAzFRS-1. The mutated residues are indicated in yellow in the pCNFRS/pCNF complex crystal structure (left). Shown is the close-up view of the active site residues with the mutation I176L (yellow) and pCNF substrate (red) (right). PDB ID: 3QE4. (D) The mutation I176L is largely responsible for pAzF selectivity in pAzFRS-1. Cells expressing pAzFRS-1, parental enzyme pCNFRS, or pCNFRS with single mutations K90Q/I176L/R257W/E272V, its cognate tRNACUATyr, and sfGFP-2TAG were grown in LB media containing pAzF (1 mM) or pCNF (1 mM). Incorporation efficiencies were evaluated by monitoring sfGFP fluorescence. Normalized fluorescence intensities were calculated from fluorescence readings at 24 h time points divided by absorbance at 600 nm. Mean values and standard deviations were calculated from three replicates.