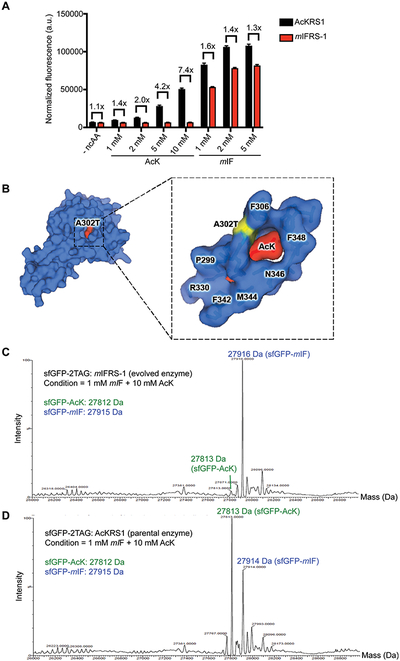
Figure 4.
Directed evolution of mIF-selective aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. (A) The variant mIFRS-1 is more selective for mIF compared to parental enzyme AcKRS1. Cells expressing mIFRS-1 or AcKRS1 with its cognate tRNACUAPyl and sfGFP-2TAG were grown in LB media containing varying concentrations of indicated ncAAs. Incorporation efficiencies were evaluated by monitoring sfGFP fluorescence. Normalized fluorescence intensities were calculated from fluorescence readings at 24 h time points divided by absorbance at 600 nm. Mean values and standard deviations were calculated from three replicates. (B) A single amino acid substitution (A302T) was found in mIFRS-1. The mutated residue is indicated in yellow in the AcKRS1/AcK complex crystal structure (left). Shown on the right is the close-up view of the active site residues with the mutation A302T (yellow) and AcK substrate (red). PDB ID: 4Q6G. (C) mIFRS-1 produces highly pure mIF-incorporated sfGFP proteins in the presence of AcK (10 mM) and mIF (1 mM). ESI-MS spectrum of purified full-length intact sfGFP. (D) AcKRS1 produces a mixture of mIF-incorporated and AcK-incorporated sfGFP proteins in the presence of AcK (10 mM) and mIF (1 mM). ESI-MS spectrum of purified full-length intact sfGFP.