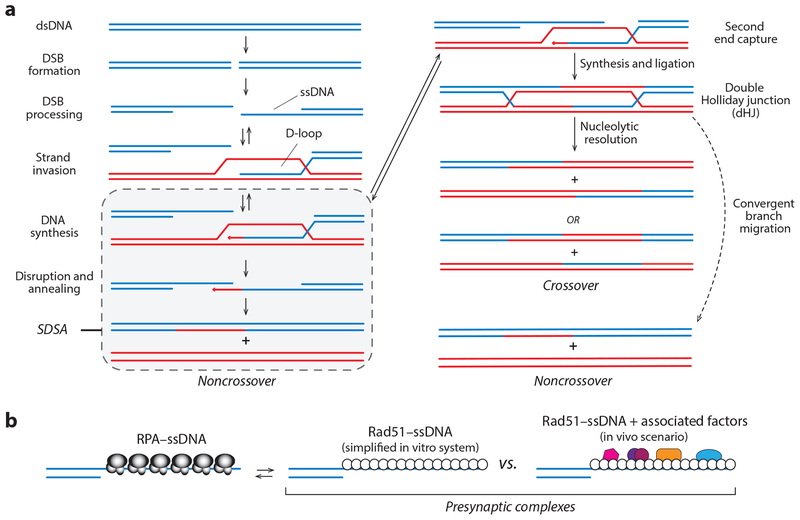
Figure 1.
(a) HR is initiated by 5′→3′ resection of the DNA ends. The ssDNA overhangs are paired with a homologous dsDNA that is used as atemplate for repair. In mitotic cells, these intermediates are normally channeled through the SDSA pathway. Alternatively, the second ssDNA can also pair with the dsDNA, leading to formation of a dHJ, which can be resolved through convergent branch migration to yield noncrossovers or cleaved by nucleases to yield crossovers. (b) Early nucleoprotein complexes in HR. The 3′ ssDNA overhangs are first bound by RPA, which is then displaced by Rad51 to form the presynaptic complex. In vitro, Rad51–ssDNA can serve as a minimal system for promoting strand invasion. In vivo, the presynaptic complex comprises Rad51 plus numerous cofactors (reviewed in 60, 67, 87, 101, 127). Abbreviations: dHJ, double Holliday junction; DSB, double-strand break; dsDNA, double-stranded DNA; HR, homologous recombination; RPA, replication protein A; SDSA, synthesis-dependent strand annealing; ssDNA, single-stranded DNA.