Figure 2. Hypersensitivity of triggerhappyp400 Mutants Caused by cyfip2 Mutations and Rescued by Conditional Cyfip2-GFP Expression.
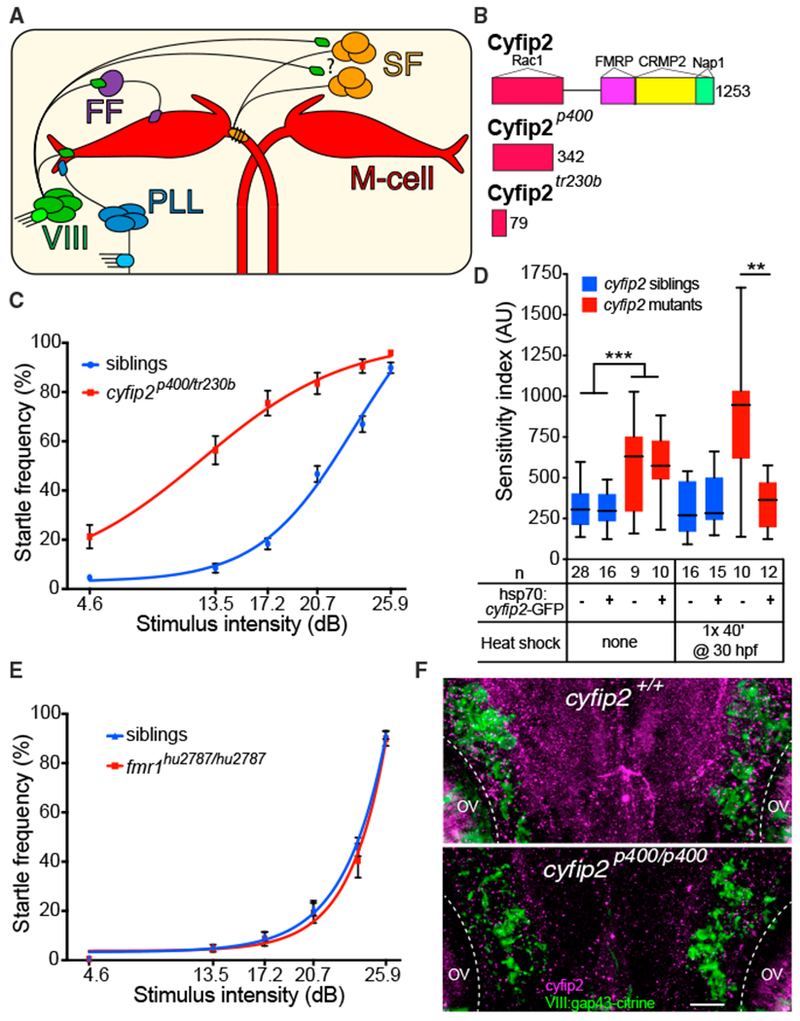
(A) Acoustic startle circuit. Acoustic nerve (VIII), posterior lateral line nerve (PLL), feedforward (FF) inhibitory, and excitatory spiral fiber (SF) neurons connect to the Mauthner cells (red).
(B) Cyfip2 protein interaction domains (Abekhoukh and Bardoni, 2014; Pittman et al., 2010). triggerhappyp400 (cyfip2p400) mutants have a premature stop codon after 342 of 1,253 amino acids. The previously identified nevermind (cyfip2tr230b) mutation (Pittman et al., 2010) is shown.
(C) Startle sensitivity curves of siblings and trans-heterozygous (trans-het) larvae from cyfip2p400/+ X cyfip2tr230b/+ crosses (n = 75 siblings, 34 trans-hets; mean ± SEM).
(D) Startle sensitivity index in cyfip2p400 sibling and mutant larvae expressing Tg(hsp70:cyfip2-GFP). Larvae were given no heat shock or one 40-min heat shock at 30 hpf. Cyfip2-GFP fluorescence was largely restricted to the CNS and was visible 90 min after heat shock, peaked around 3 hr after heat shock, and was detectable at low levels 24 hr later (Figure S3C). Without a heat shock, cyfip2p400 mutants had increased startle sensitivity (***p < 0.001, Mann-Whitney test), whereas heat shock reduced the sensitivity of cyfip2 mutants with the transgene compared with those without it (**p < 0.01, Mann-Whitney test).
(E) Startle sensitivity curves for fmr1 sibling (n = 62) and mutant larvae (fmr1hu2787/hu2787, n = 20) at 5 dpf (mean ± SEM).
(F) Hindbrain expression of Cyfip2 in 5 dpf wild-type (cyfip2+/+) and mutant (cyfip2p400/p400) larvae using a Cyfip2 antibody (Ab). Membranes of VIII neurons are marked by Tg(SCP1:Gal4FF(y256Et)); Tg(UAS:gap43-citrine) and anti-GFP Ab. Dashed lines indicate the otic vesicles (OVs). Scale bar, 10 μm.
