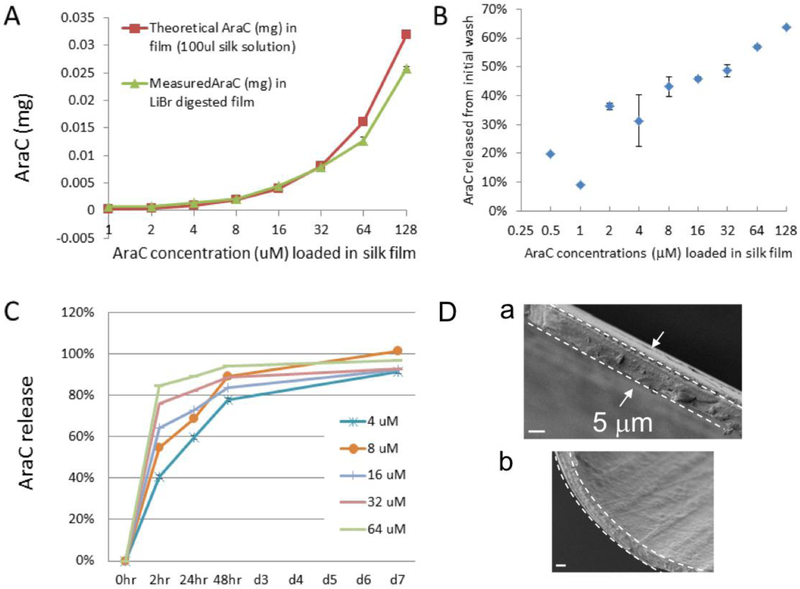
Figure 1: Release profile of arabinofuranosylcytidine (AraC) from silk films in vitro.
AraC content was measured with a spectrophotometer of absorbance at 272 nm. (A) Comparison of original loading doses (red line) with recovered AraC doses after dissolving silk films in LiBr (9.3 mL) (green line), indicating that most of loaded drugs were retained in silk films. (B) Percentage of AraC release during the step of poly-lysine coating of silk films, showing drug loss in proportion to the initial loading doses. This loss had been subtracted from the loading doses to reflect the actual retained amount of drug in silk films for cell culture studies (see Method). (C) Release profile of postprocessed AraC-silk films, showing a fast release within the first 2 hours and slower release up to days in vitro 7 (DIV7). (D) Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) images of silk films showing the cross-section (demarcated by the dashed lines in a & b) and the surface (b). Scale bar, 3 μm.