Figure 7.
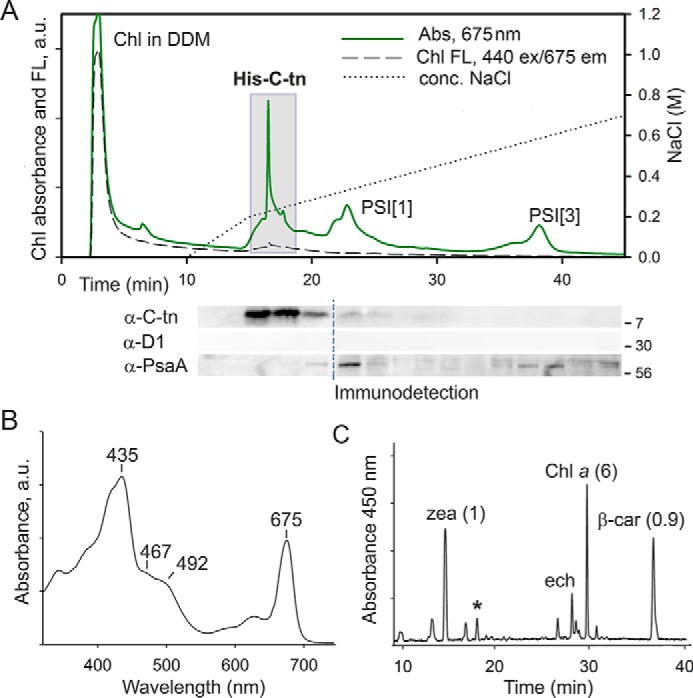
The C-terminal segment of FeCh lacking the catalytic domain (an artificial His-C-tn protein) binds Chl, β-car, and zeaxanthin in vivo. A, the His-C-tn protein was expressed in the Synechocystis hemH-Δ324 genetic background and purified on a nickel column. The obtained eluate was further separated by anion-exchange chromatography, and the Chl absorbance (675 nm) and Chl fluorescence were recorded (Chl FL; 440-nm excitation/675-nm emission). Note the strikingly different emission intensity of Chls in DDM micelles and Chls bound to His-C-tn. Minute fractions were collected and separated by SDS-electrophoresis, and the presence of His-C-tn protein was detected by antibodies raised against the FeCh C terminus. The core photosystem I and II subunits PsaA and D1 were also immunodetected as a control of purity; dashed line indicates blot splicing. Fractions highlighted by the gray box were pooled and used for the analysis of pigments associated with His-C-tn. B, the absorption spectrum of the His-C-tn protein purified by a combination of nickel-affinity and anion-exchange chromatography as described above. C, the extracted pigments from the purified His-C-tn protein were separated on a C18 column; the molar stoichiometry of the major constituents is indicated. zea, zeaxanthin; ech, echinenone. The unknown carotenoid (see Fig. 2D) is marked by an asterisk.
