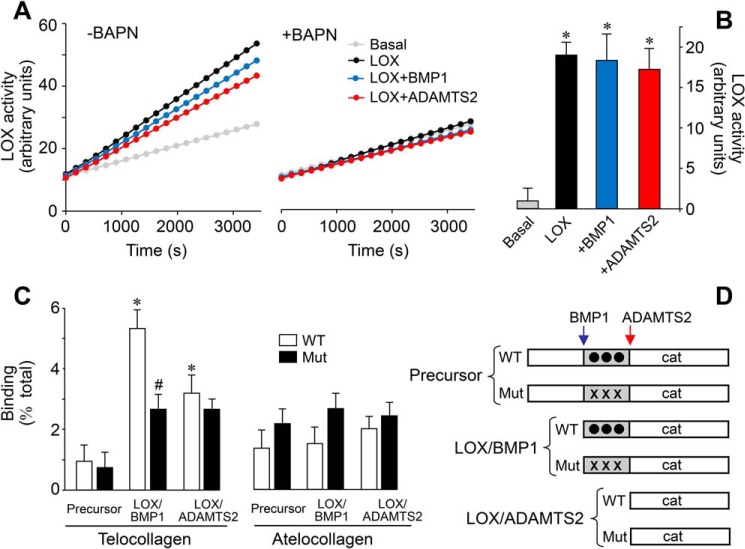
Figure 8.
Effect of the proteolysis of LOX on enzymatic activity and collagen-binding capacity. Supernatants from LOX-overexpressing cells under control conditions (LOX) or exposed to BMP1 or ADAMTS2 were assessed for LOX enzymatic activity in a time-lapse fluorescence assay performed in the absence (left panel) or presence (right panel) of the LOX inhibitor BAPN (0.3 mm). Basal tracing represents the activity from a supernatant of a culture in the absence of induction with doxycycline. Representative data (A) and quantification from three independent experiments (B) are shown. Values are shown as fluorescent arbitrary units (mean ± S.D., n = 6, *, p < 0.05 versus basal). C, solid-phase binding assay to telocollagen (with intact telopeptides) or atelocollagen (without telopeptides) of the various LOX species shown in D. Binding capacity is shown as percentage of total (mean ± S.D., n = 6, *, p < 0.05 versus the corresponding control without protease treatment, #, p < 0.05 versus the corresponding WT). Statistical comparisons between groups were calculated by one-way ANOVA analysis followed by Bonferroni's post test.