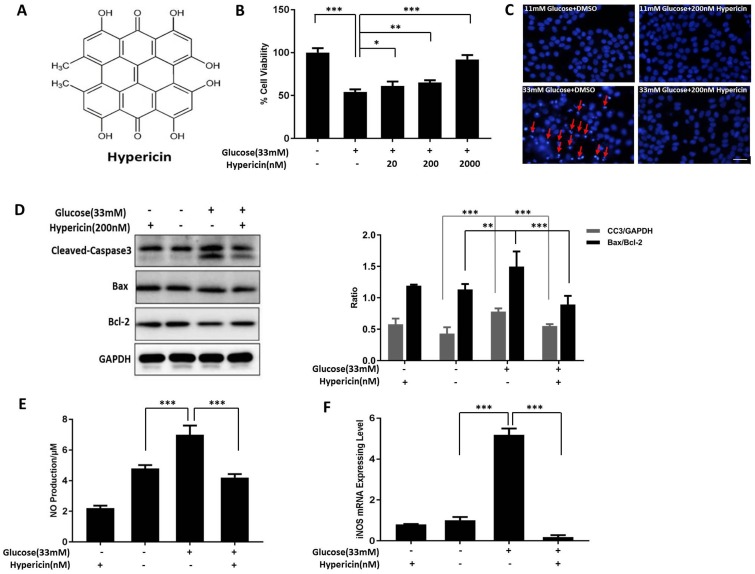
Figure 1.
Hypericin inhibits apoptosis and NO production in INS-1 cells under high-glucose toxicity. (A) Chemical structure of hypericin. (B) Measurement of cell viability by an MTT assay. INS-1 cells were treated with 33 mM glucose in the absence or presence of hypericin (20, 200, and 2000 nM) for 72 h and then subjected to the MTT assay. INS-1 cells treated with 11 mM glucose were used as the control. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 3). (C) Detection of apoptotic bodies by DAPI staining. INS-1 cells were treated with 33 mM glucose, 200 nM hypericin or a combination of the two for 72 h. The cells were then stained with DAPI and observed under a fluorescence microscope. Arrows indicate the apoptotic bodies. Scale bar 50 μm. The results are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Detection of apoptosis-related proteins by Western blot. INS-1 cells were treated as in (C). Then, the protein levels of cleaved-caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 were determined by Western blot; GAPDH was used as a loading control. Density ratios of CC3 to GAPDH or Bax to Bcl-2 as measured with ImageJ are shown in the two right-hand panels. The experiment was repeated three times. (E) Detection of NO production. INS-1 cells were treated as in (C). Production of NO was detected by the Griess reaction in culture medium. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 3). (F) Detection of iNOS mRNA levels by RT-qPCR. INS-1 cells were treated as in (E), after which total RNA was extracted and iNOS mRNA was amplified by conventional SYBR Green real-time PCR analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 3). NO, nitric oxide; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; MTT, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Bax, Bcl-2-Associated X protein; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-2. Experiments were repeated three times. * p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001 versus the high-glucose group.