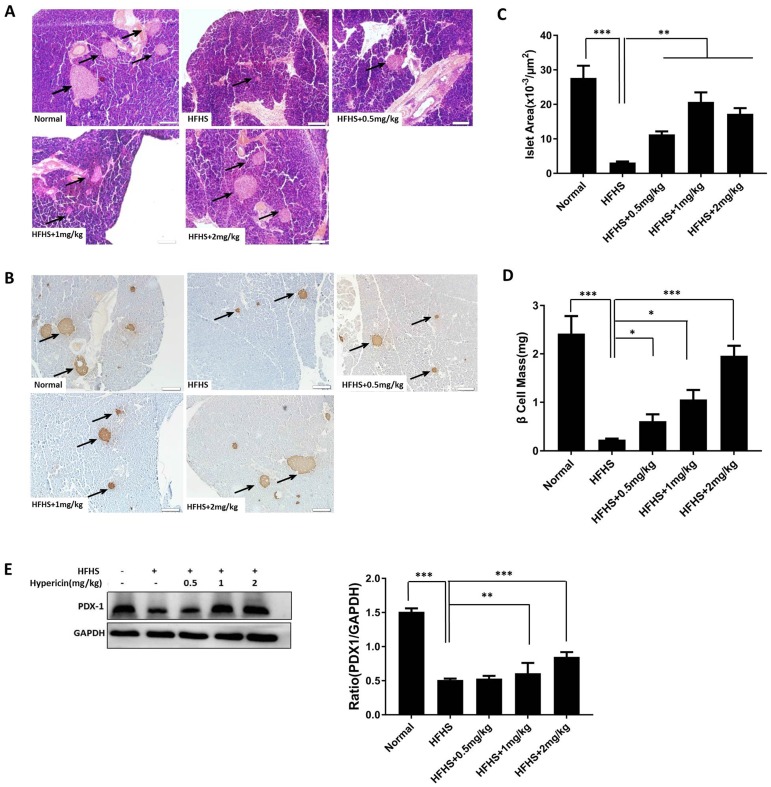
Figure 5.
Prophylactic use of hypericin decreases β-cell loss and maintains islet mass in HFHS-fed mice. (A) Histological sections of mouse pancreatic tissue. After sacrifice, the mouse pancreases were removed and weighed. Portions of the mouse pancreases from (A) were fixed and subjected to HE staining. The scale bar represents 100 μm. Arrows indicate pancreatic islets. (B) IHC analysis of the mouse pancreas using anti-C-peptide antibodies. Portions of the mouse pancreases from (A) were fixed and subjected to IHC analysis. The scale bar represents 100 μm. Arrows indicate positively stained cells. (C) Measurement of islet area in the mouse pancreas. Pancreatic sections subjected to IHC staining with an anti-C-peptide antibody in (B) were used to measure the islet area of the pancreas. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 8). (D) Calculation of β-cell mass of the pancreas. Pancreatic sections that were IHC stained with an anti-C-peptide antibody in (B) were used to calculate the β-cell mass of the pancreas. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 8). (E) PDX1 protein levels in the mouse pancreas. Portions of the mouse pancreases from (A) were homogenized, and total cellular lysates were prepared and subjected to Western blots using anti-PDX1 antibodies. GAPDH was used as a loading control. The density ratios of PDX1 to GAPDH were measured by ImageJ, and the fold change relative to the normal group is shown in the right-hand panel. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 6). * p< 0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 versus the HFHS group.