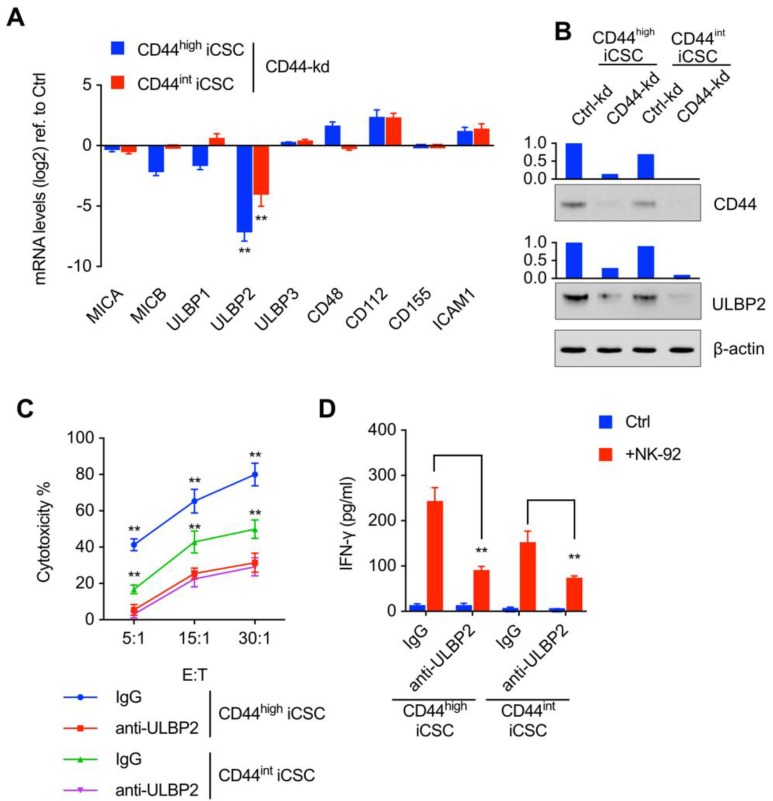
Figure 2.
CD44 regulated ULBP2 expression, which then further influenced the susceptibility of CSCs to NK cell mediated cytotoxicity. (A) MICA/B, ULBP1-3, CD48, CD112, CD155, and ICAM1 transcript levels of CD44highiCSC/CD44intiCSC stably expressing dCas9-KRAB and sgRNA against CD44 (CD44-knockdown, CD44-kd) were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Levels are represented relative to those found in control-infected cells as means ± SD (n=3) (**: p < 0.01). (B) CD44 and ULBP2 protein levels of identical cells (Fig. 2A) were analyzed by Western blotting. β-actin served as a loading control. (C) CD44highiCSC and CD44intiCSC were used in the 4 hours NK cell cytotoxicity assay with NK-92 cells at different E:T ratios. Assays were performed either in the presence of M311 mAb (anti-ULBP2) or control IgG. Data are showed in means ± SD from three independent experiments which are performed in triplicate (**: p < 0.01). (D) IFN-γ release in the supernatants of cytotoxic assay (Fig. 2C, E:T ratio = 15:1) was determined by ELISA. Data were presented as mean ± SD (n=3) (**: p<0.01).