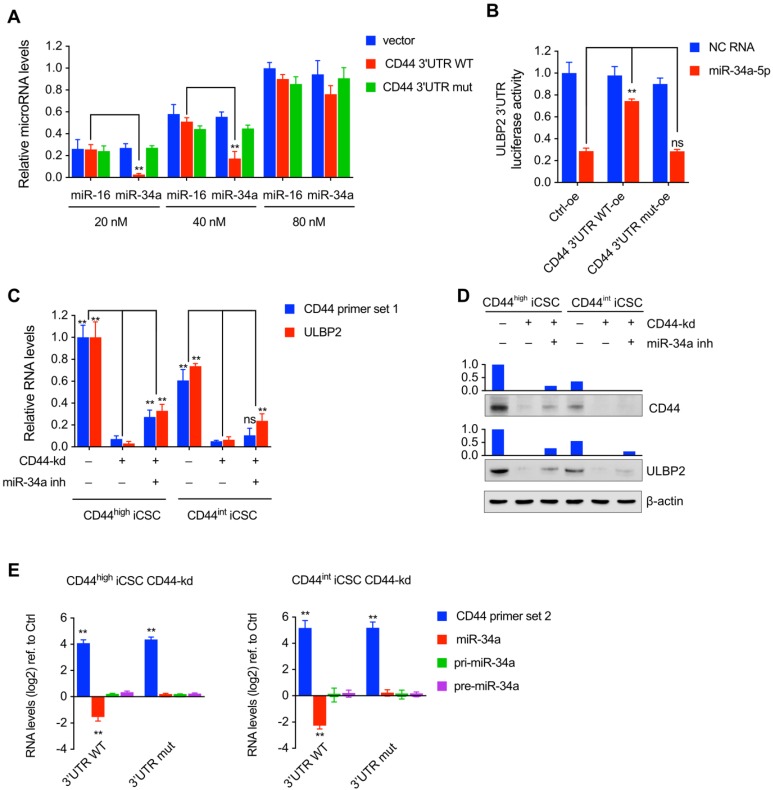
Figure 6.
CD44 functioned as a ceRNA to protect ULBP2 in liver CSCs by competitively binding miR-34a. (A) miR-16 and miR-34a concentrations in saturation assays were determined by qRT-PCR. microRNA levels were represented as means ± SD (n=3) (**: p < 0.01). (B) CD44 3'UTR overexpressing vector and ULBP2 3'UTR containing pGL3-Promoter vector were transfected in 293T cells together with miR-34a-5p mimics and pRL-CMV. Luciferase activity of ULBP2 3'UTR were determined by luciferase reporter assay. (C) CD44highiCSC/CD44intiCSC stably expressing dCas9-KRAB and sgRNA against CD44 (CD44-knockdown, CD44-kd) were transfected with negative control or miR-34a inhibitor. CD44 and ULBP2 transcript levels were determined by qRT-PCR. Levels are represented relative to those found in control- transfected cells as means mean ± SD (n=3) (ns: not significant, **: p < 0.01). (D) CD44 and ULBP2 protein levels of identical cells (Fig. 6C) were analyzed by Western blotting. β-actin served as a loading control. (E) CD44highiCSC/CD44intiCSC stably expressing dCas9-KRAB and sgRNA against CD44 (CD44-knockdown, CD44-kd) were transfected with CD44 3'UTR WT expression vector or CD44 3'UTR mut expression vector. CD44 3'UTR, miR-34a, pri-miR-34a, and pre-miR-34a transcript levels were determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to Ctrl (blank expression vector). Levels are represented relative to those found in control- infected cells as means mean ± SD (n=3) (ns: not significant, **: p < 0.01).