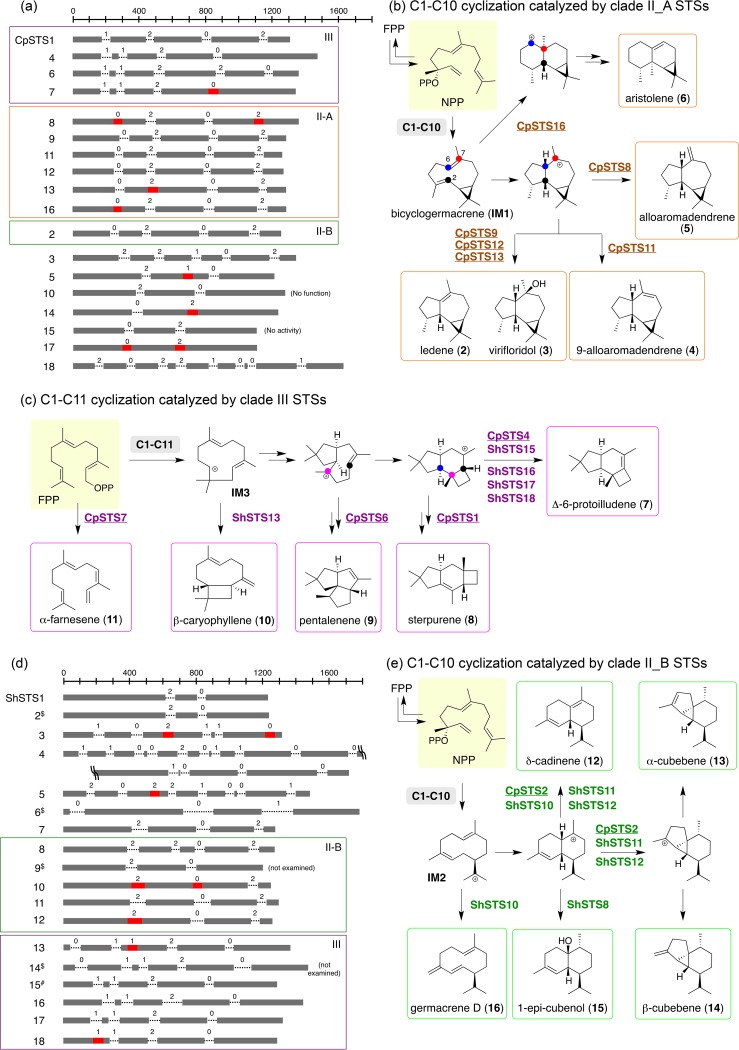
FIG 3.
(a) Schematic view of the gene structures of CpSTSs. The dark bars indicate exons and the dotted lines introns along with intron phases. The red bars represent the computationally predicted introns that were not spliced (skipped) in cDNA from A. oryzae TFs, removal of which resulted in functional STS expression in the E. coli TF. Genes with the colored boxes are proposed paralogs or orthologs in C. pseudo-pinsitus and S. hirsutum that belong to cyclization clade III (purple), II_A (orange), or II_B (green). Nonfunctional refers to CpSTS10 lacking conserved active-site motifs. (b) Proposed cyclization mechanism of terpene products catalyzed by clade II_A STSs. (c) Proposed cyclization mechanism of terpene products catalyzed by clade III STSs. (d) Schematic view of the gene structures of ShSTSs. #, gene structure of a functional ShSTS15 that was reported previously (35). $, computationally predicted gene structure of an STS not investigated in this work. (e) Proposed cyclization mechanism of terpene products catalyzed by clade II_B STSs. STSs from C. pseudo-pinsitus are underlined in panels b, c, and e. Stereochemistries of putative carbocation intermediates are predicted by those of cyclized products.