Figure 3. Regulatory sequence of the pBR327-Lrh(WT)GFPuv vector and outcome of GFPuv reporter assay.
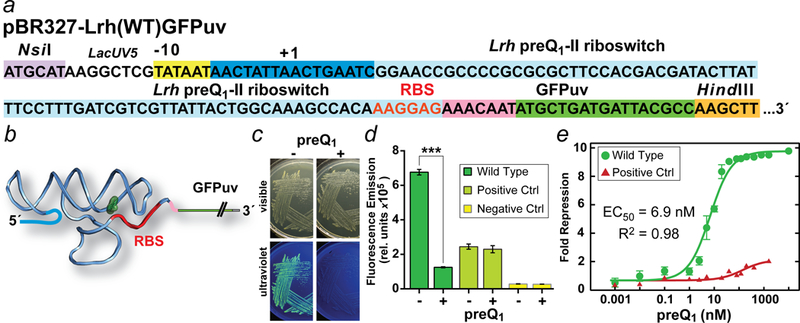
(a) DNA sequence of the pBR327 lacUV5 promoter showing the Pribnow box (yellow) and approximate transcription start site at +1. The wild-type Lrh sequence corresponding to the COG4708 gene13 extends from the −10 box to the GFPuv start codon (green) and comprises multiple regions: the 5´-leader (dark blue box); the preQ1-II riboswitch (powder blue box); the RBS (red letters); and a short linker (pink box) that separates the RBS from GFPuv (green box). The GFPuv gene starts at ATG, which replaces the start site of the naturally occurring Lrh queT gene. Unique restriction sites for sub-cloning the Lrh riboswitch sequence are shown. (b) Schematic diagram for the gene “off” Lrh riboswitch transcript from a depicting sequestration of the RBS. (c) E. coli strain JW2765 ΔqueF harboring the pBR327-Lrh(WT)GFPuv vector plated on CSB agar in the presence (2 μM) and absence of preQ1. Under white light cells grow similarly at 37 °C but show fluorescence differences attributable to GFPuv expression under a handheld UV lamp at 365 nm. (d) Reporter assay analysis of preQ1-mediated repression of GFPuv protein expression. Cells were grown in CSB media with 1 μM preQ1 or no preQ1 to assess difference in GFPuv fluorescence emission from the wild-type reporter and control constructs. Each pair was analyzed statistically. The mean and standard deviation of three independent readings are reported. The wild-type reporter probability (P) equals 0.0002 based on an unpaired, two-tailed Welch’s t-test (t = 51; df = 2.16). ***P < 0.001 is statistically highly significant. Controls ± preQ1 but lacking the riboswitch were not statistically different (P >0.05). (e) The fold repression for the on and off states of the wild-type reporter was calculated and dose-response curve was fit to give an approximate EC50. Measurements were conducted as in d. Similar analysis was conducted on the positive control, which showed <2-fold repression.
