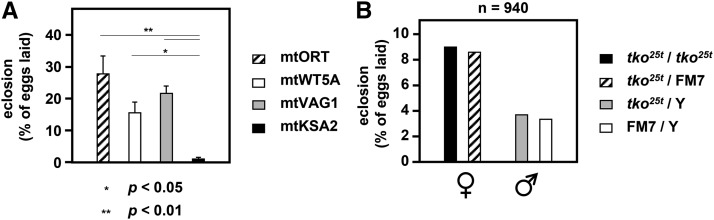
Figure 3.
Eclosion frequency of nORT cybrids cultured on medium containing antimycin A (A) Egg-to-adult eclosion frequency (i.e., percentage of eggs completing development and emerging as adults) of the indicated cybrid lines, cultured in 5 μg/ml antimycin A. Note that all emerging flies in a given culture were of the same genotype. Means ± SEM of 7 or 8 replicate vials (∼65 eggs laid per vial). Significant differences based on one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD test. The dose of antimycin was based on preliminary trials to confirm the sub-lethal concentration inferred from the literature (Frei et al. 2005). (B) Egg-to-adult eclosion frequency for progeny flies of each genotype indicated, in the cross tko25t / FM7 x tko25t / Y, cultured on medium containing 5 μg/ml antimycin A. The flies used in the cross were all in the control mtDNA background mtWT5A. Note that males were more severely affected by the drug than females (which was observed for all genotypes tested), but the proportion of flies of a given sex eclosing on antimycin A was independent of tko genotype (chi-squared test, P > 0.05 for both sexes). Data are from a single, large-scale experiment (n = 940) of sufficient size to generate statistically robust values.