Figure 1.
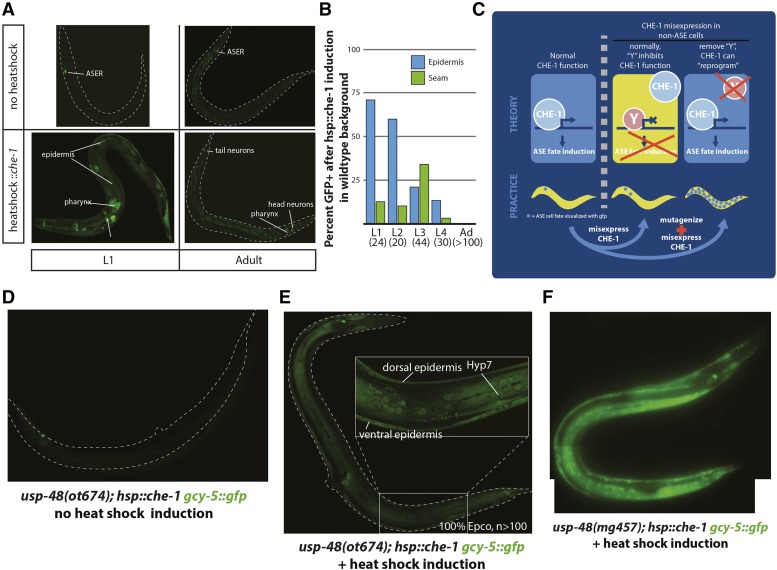
Basic parameters of the screening approach and isolation of the first mutant. A: Ectopic expression of che-1 in an otherwise wild-type genetic background has diminished activity as development progresses. Without heatshock, gcy-5::gfp (ntIs1) is expressed solely in the ASER neuron. Heatshock induction of che-1 during the early L1 stage results in broad activation of the gyc-5 promoter, with GFP observed in the epidermis, pharnyx, multiple neurons, and other tissues. Heatshock during the adult stage is restricted to a few pharyngeal cells and extra neurons in the head and tail. B: Quantification of the results shown in panel A. Numbers below stage indicate animals scored. C: Outline for screening strategy and underlying hypothesis. che-1 functions normally as a terminal selector transcription factor in the ASE neurons, and activates expression of multiple genes including gcy-5. If ectopically expressed in adult tissues, most tissues are refractory to activation of gcy-5 target. It is hypothesized that some factor or factors, “Y”, prevent CHE-1 from activating gcy-5 and other targets. This screen aims to identify the factor or factors “Y” by mutagenesis, with the resultant phenotype expected to be ectopic expression of gcy-5 and other targets outside of what is normally seen in unmutagenized animals. D: Without ectopic induction of CHE-1, usp-48(ot674) animals express gcy-5::gfp only in ASER as in wild-type animals. E: After animal-wide heatshock induction of CHE-1, the usp-48(ot674) animals exhibit strong gcy-5::gfp expression specifically in the epidermis. F: mg457 is another nonsense allele of usp-48 and phenocopies ot674.