Figure 3.
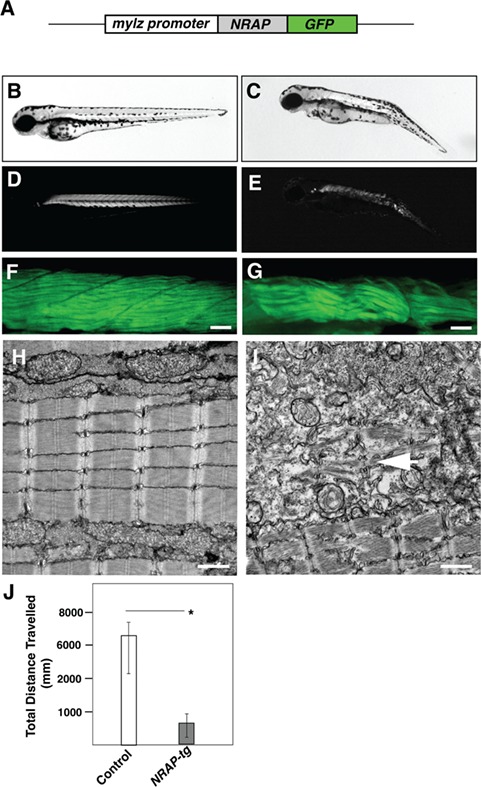
Transgenic NRAP zebrafish exhibit structural and functional deficits. (A) Schematics of NRAP transgenic construct. Human NRAP cDNA was cloned in-frame with GFP reporter and downstream of the zebrafish myosin light chain promoter using tol2-transgenesis. (B and C) Tg (mylz:NRAP-gfp) fish exhibit dorsal curvature and leaner bodies indicative of a myopathic phenotype (3dpf) (D and E) Visualization of Tg (mylz:NRAP-gfp) under polarized light revealed reduced birefringence compared to control (3 dpf). (F and G) Whole-mount phalloidin staining of Tg (mylz:NRAP-gfp) larvae (3 dpf) exhibiting fewer myofibers and smaller myotomes in comparison to controls. Scale bar: 50 μm. (H and I) Transmission electron microscopy demonstrating mature myofibers in control fish whereas Tg (mylz:NRAP-gfp) fish exhibit presence of immature sarcomeres (white arrow) and lacked matured myofibrils (arrow). Scale bar: 500 nm. (J) Quantification of the distance traveled by control (n = 55–75) and Tg (mylz:NRAP-gfp) (n = 28–44), acquired by an automated infra-red imager. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. from three different experiments. P-values were calculated using a two-tailed Mann–Whitney U-test, *P < 0.01.
