Table 2.
Substrate scope of 4‐hydroxybenzoate decarboxylases (EC 4.1.1.61), protocatechuate decarboxylases (EC 4.1.1.63), gallate decarboxylases (EC 4.1.1.59) and vanillate decarboxylases (no EC number assigned). Substrates with highest activities are marked with an asterisk (*).
| Organism (enzyme name) | Accepted substrates |
Tested non‐ substrates |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4‐Hydroxybenzoate decarboxylases | |||
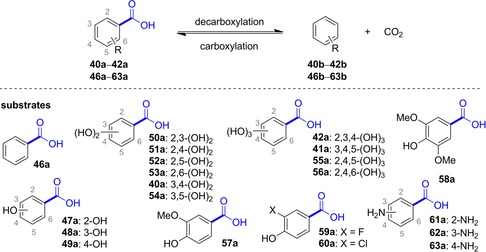
| Sedimentibacter hydroxybenzoicus JW/Z1 (basonym Clostridium hydroxybenzoicum)[b,c,d] | 49a,*[e] 40a,[e] 57a, 59a, 60a | 47a, 48a, 50a, 51a, 52a, 42a, 41a | 66 |
| Cryptoanaerobacter phenolicus [c,d] | 49a | 48a | 67 |
| Enterobacter cloacae P240 (4‐HBD)[b] | 49a,*[e] 40a | 46a, 47a, 48a, 53a, 56a, 41a, 57a, 63a | 68 |
| B. subtilis (BsdBCD)[a] | 49a,*[e] 57a [e] | – | 65, 69 |
| E. coli O157:H7 (EcdCD)[a] | 49a,*[e] 57a [e] | – | 65, 70 |
| Salmonella typhimurium (StdBCD)[a] | 49a,*[e] 57a [e] | – | 65 |
| Chlamydia pneumoniae AR39[b,d] | 49a [e] | 51a | 71 |
| Klebsiella aerogenes (Klebsiella pneumoniae) (KpBCD)[a,c] | 49a,*[e] 52a, 40a, 41a, 57a [e] | 46a, 47a, 48a, 50a, 51a, 53a, 54a, 42a, 61a, 62a, 63a, 56a | 65, 72 |
| Desulfovibrio sp./Methanospirillium hungatei consortium[b,d] (two decarboxylases, one carboxylase) | 49a,* 41a, 59a, 60a | – | 73 |
| Clostridium thermoaceticum (basonym Moorella thermoacetica)[b,c,d] | 49a,* 40a, 57a, 60a, 59a | 46a, 47a, 48a, 50a, 51a, 52a, 53a, 54a, 41a, 58a | 74 |
| Protocatechuate decarboxylases | |||
| Enterobacter cloacae P240 (EcAroY)[b] | 40a [e] | – | 75 |
| Sedimentibacter hydroxybenzoicus JW/Z1 (basonym Clostridium hydroxybenzoicum) (3,4‐DHBD)[b,c,d] | 40a [e] | 47a, 48a, 49a, 50a, 51a, 52a, 42a, 41a, 57a, 59a | 66a, 76 |
| Gallate decarboxylases | |||
| Citrobacter sp.[c] | 40a, 41a,* 54a, 48a, 50a | 46a, 47a, 51a, 52a, 53a, 41a, 61a, 62a | 77 |
| Arxula adeninivorans (Agdc1p)[b] | 40a, 41a* | 48a–52a | 78 |
| Lactobacillus plantarum LpdC[a] (UbiX‐like LpdB required for activity) | 40a, 41a* | – | 79 |
| Pantoea agglomerans T71[b,d] | 41a [f] | 46a, 40a–42a, 46a–57a, 62a, 63a | 80 |
| Vanillate decarboxylase | |||
| Streptomyces sp. D7 (VcdCD)[a,b] | 57a [e] | 49a, 40a, 41a, 58a | 65, 81 |
[a] Recombinant decarboxylase expressed in E. coli.
[b] (Partially) purified from wild‐type strain.
[c] (Induced) resting cells (in vivo decarboxylation).
[d] Oxygen‐sensitive protein and/or anaerobic strain.
[e] Reverse carboxylation of the respective phenol in the presence of excess bicarbonate was demonstrated.
[f] Carboxylation was tested, but no product acid was detected.
