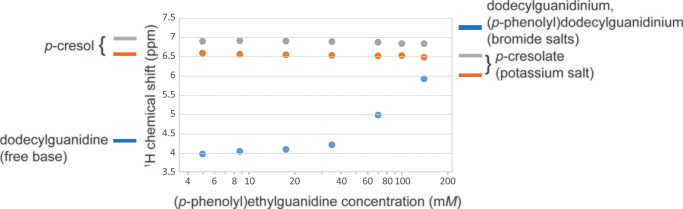
Figure 10.
Concentration dependence of the 1H chemical shifts of the phenolic ring (gray solid circle, orange solid circle) and of the guanidine group (blue solid circle), in (p-phenolyl)ethylguanidine. Average values are shown for peaks split by j–j coupling. Likewise, for the monoalkylguanidinium bromide salts, there were two to three partially resolved resonances for the guanidino group protons in the range of 6.9–7.5; these were averaged with weightings of 1:2:2 to give the plotted value of 7.25 ppm (blue line next to the right axis). Well below ∼30 mM, the chemical shifts in (p-phenolyl)ethylguanidine are nearly identical with those seen for isolated phenol and guanidine groups, indicated by lines next to the left vertical axis. The changing values over the 20–150 mM concentration range are consistent with the formation of an H-bonded dimer complex. That is, at the highest concentrations, the averaged chemical shift of the guanidine protons approaches that of dodecylguanidinium cation, whereas the phenolic ring protons move somewhat toward the values for phenolate. The latter are represented by the chemical shifts of Br– or K+ salt solutions in DMSO, respectively, as indicated next to the right axis.