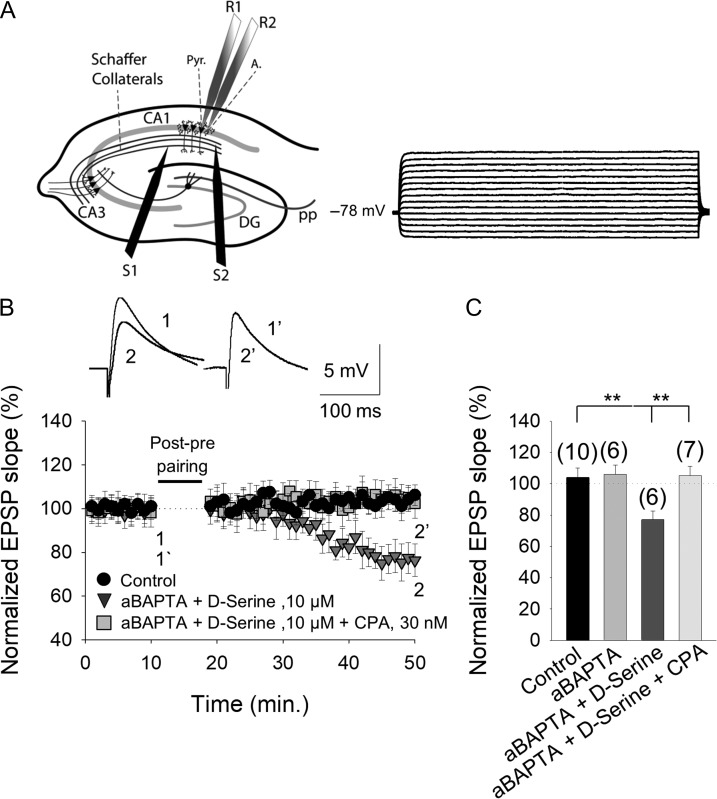
Figure 8.
The adenosine involved in preventing t-LTD at P22–P30 is from astrocytes. (A) Left, scheme showing the general experimental set-up: R1 and R2, recording electrodes; S1 and S2, stimulating electrodes; Pyr, pyramidal neuron; A, astrocyte; right, voltage responses of an astrocyte shown in current-clamp. (B) In astrocyte-neuron dual recordings, with the calcium chelator BAPTA injected into the astrocyte via the recording pipette (aBAPTA), and with D-serine (100 μM) added to the bath, a post–pre pairing protocol induced t-LTD (grey triangles) but not in control conditions (no BAPTA and no d-serine, black circles). The presence of CPA impaired the t-LTD observed with aBAPTA and d-serine (dark grey squares). Inset: representative traces at the baseline (1 and 1´) and 30 min after the pairing protocol (2 and 2´) in the presence of aBAPTA and d-serine alone, with or without CPA. (C) Summary of the results, with the error bars reflecting the S.E.M. and the number of slices shown in parentheses: **P < 0.01, unpaired Student’s t-test.