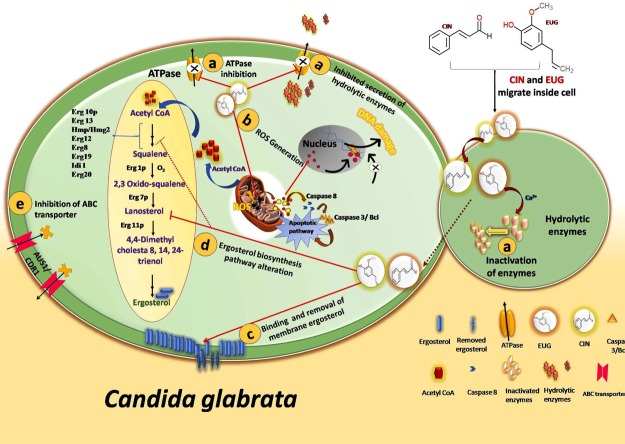
Figure 11.
Schematic diagram representing possible antifungal mechanism (a–e) of CIN and EUG in C. glabrata. (a) By inhibition of membrane ATPase pump which mediates secretion of hydrolytic enzyme or by degradation of hydrolytic enzymes; (b) by ROS generation which results in release of cyt c and activates proapoptotic pathways; (c) by disturbing cell membrane integrity via removal of membrane ergosterol; (d) by inhibiting/altering the functionality of biosynthetic pathway enzymes similar to ergosterol; and (e) by blocking import of extracellular sterol or downregulating the expression of ABC sterol importer and drug transporter.