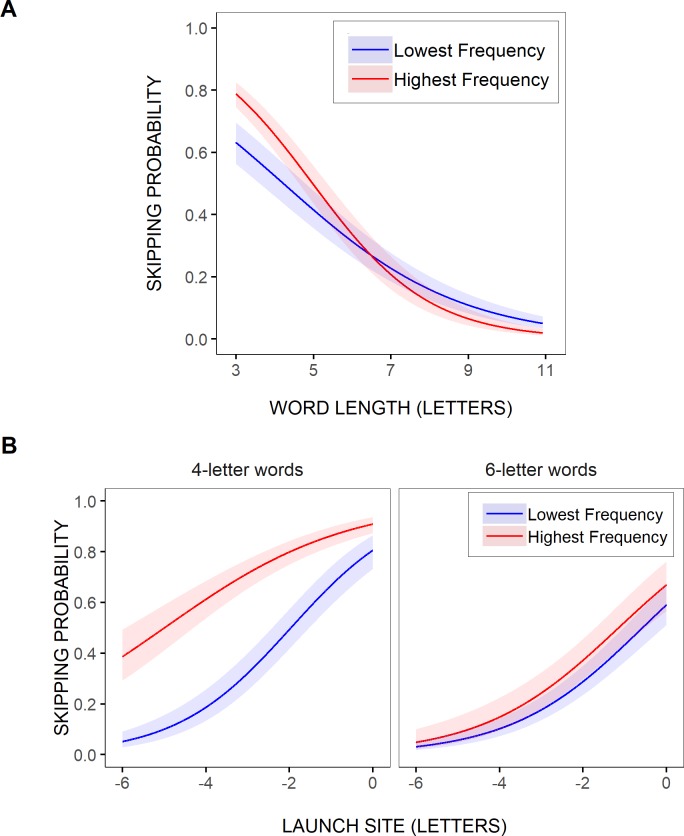
Fig 6. Estimated effect of visuo-motor and linguistic variables on word-skipping rate.
Partial effects (with 95% confidence intervals) computed from the parameters of GLMM Model 1’ (A; Table 4) and GLMM Model 2’ (B; Table 5), representing the probability of word skipping across all words in the sentences as a function of word length (A) and for 4- and 6-letter words as a function of saccadic launch-site distance (in letters relative to the space in front of the words; B), separately for the two most extreme (i.e., the lowest vs. the highest) word-frequency values across all words selected for analysis (0.01 and 9.59 log units respectively).