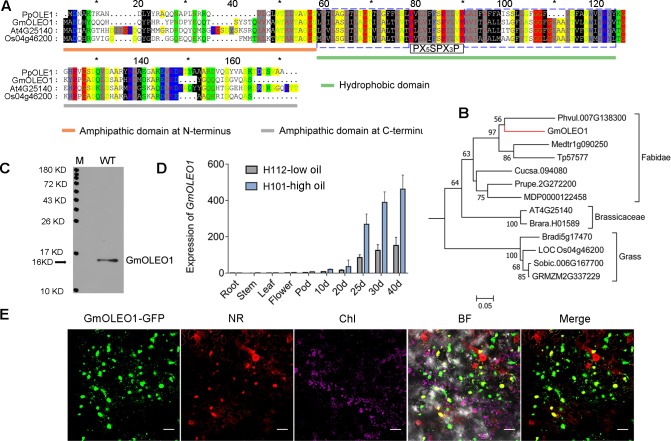
Fig 2. Sequence and expression analysis of GmOLEO1.
A, Domain structure and full-length amino acid alignment of representative OLE protein orthologs, including the structurally well-studied PpOLE1 (Physcomitrella patens), GmOLEO1, At4G25140 (Arabidopsis thaliana), and Os04g46200 (Oryza sativa). The amphipathic domains at the N-terminus and C-terminus are highlighted by blue and gray solid boxes, respectively. The conserved hydrophobic domain between two amphipathic proteins is shown by a red solid box. Dotted boxes indicate the two hydrophobic arms that can form a hairpin (blue in D); (PX5SPX3P) indicate the conserved sequence that forms a loop (black in D). B, Phylogenetic relationship between GmOLEO1 and its orthologs. All amino acid sequences were retrieved from Phytozome (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov). C, Gel image showing the molecular mass of GmOLEO1 (15.76 KD) using Western blot. M, protein marker, WT, proteins extracted from developing seeds of Williams 82 at 40 DAF. D, The relative transcript level of GmOLEO1 in different soybean tissues and developing seeds at 10, 20, 25, 30, and 40 days after flowering between the high-oil soybean cultivar H101 and low-oil cultivar H112; ** P<0.01 t-test. E, Subcellular localization analysis of GmOLEO1. GmOLEO1-GFP signal (GFP) colocalizes with oil bodies stained with Nile Red (NR). Chl represents chloroplast, BF represents bright field, and Merge shows both GFP and NR. Scale bar, 20 μm. White arrows indicate oil bodies.