Figure 1.
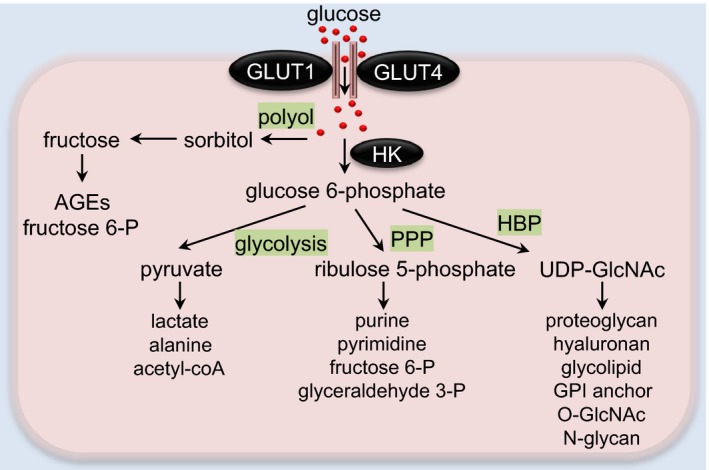
Glucose metabolic pathways in the heart. In cardiomyocytes, glucose is transported through glucose transporters GLUT1 or GLUT4. Polyol pathway‐derived sorbitol and fructose may be converted to AGEs or fructose 6‐P for glycolytic use. Intracellular glucose can be phosphorylated to glucose 6‐phosphate by hexokinase (HK). Glucose 6‐phosphate is then metabolized bv multiple pathways, including glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), and hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP). In the cytosol, pyruvate can be utilized to form alanine or lactate. In mitochondria, pyruvate is converted to acetyl‐CoA for the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Ribulose 5‐P derived from PPP can be used for pyrimidine/purine synthesis or converted into intermediates of glycolysis. UDP‐GlcNAc, the final product of HBP, serves as a substrate for the synthesis of proteoglycans, hyaluronan, glycolipid, GPI anchor, O‐GlcNAc modification, and N‐glycan. AGEs indicates advanced glycation end products; fructose 6‐P, fructose 6‐phosphate; GLUT, glucose transporter; glyceraldehyde 3‐P, glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate; GPI, glycosylphosphatidylinositol; O‐GlcNAc, O‐linked β‐N‐acetylglucosamine; ribulose 5‐P, ribulose 5‐phosphate; UDP‐GlcNAc, uridine diphosphate N‐acetylglucosamine.
