Figure 2.
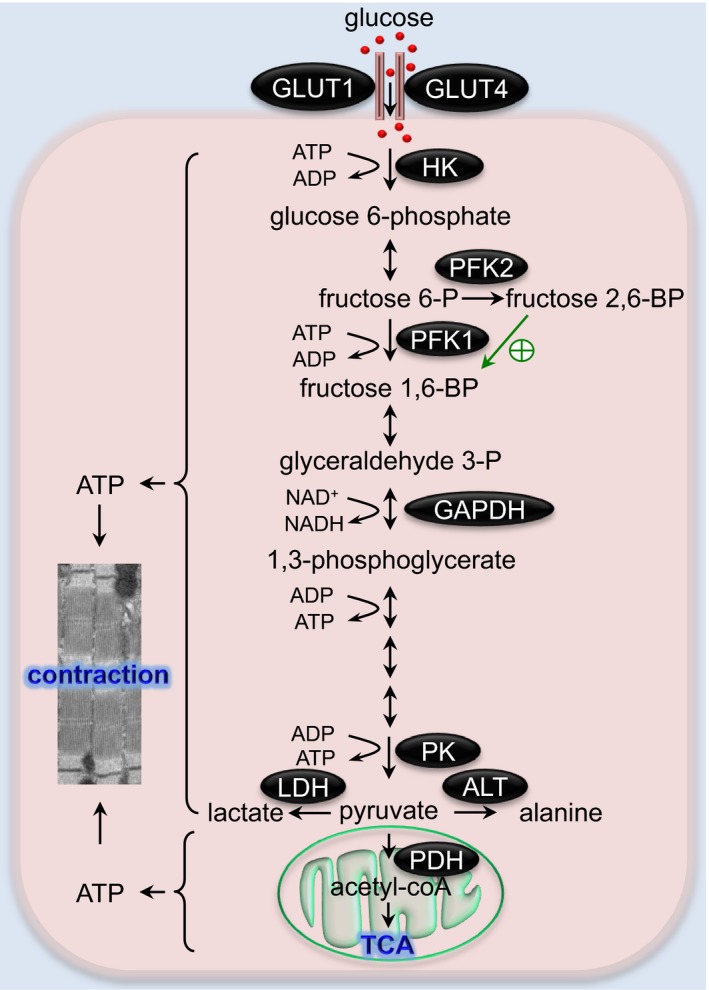
The glycolysis pathway in the heart. A series of enzymatic reactions of glycolysis convert glucose to pyruvate, which may be reduced to lactate or further catabolized by the TCA cycle. Glycolysis‐derived ATP plays a crucial role in maintaining the contractile function of the heart. The green arrow indicates activation of PFK1 by fructose 2,6‐biphosphate. ALT indicates alanine transaminase; fructose 1,6‐BP, fructose 1,6‐bisphosphate; fructose 2,6‐BP, fructose 2,6‐bisphosphate; fructose 6‐P, fructose 6‐phosphate; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; GLUT, glucose transporter; glyceraldehyde 3‐P, glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate; HK, hexokinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PFK, phosphofructokinase; PK, pyruvate kinase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid.
