Figure 1.
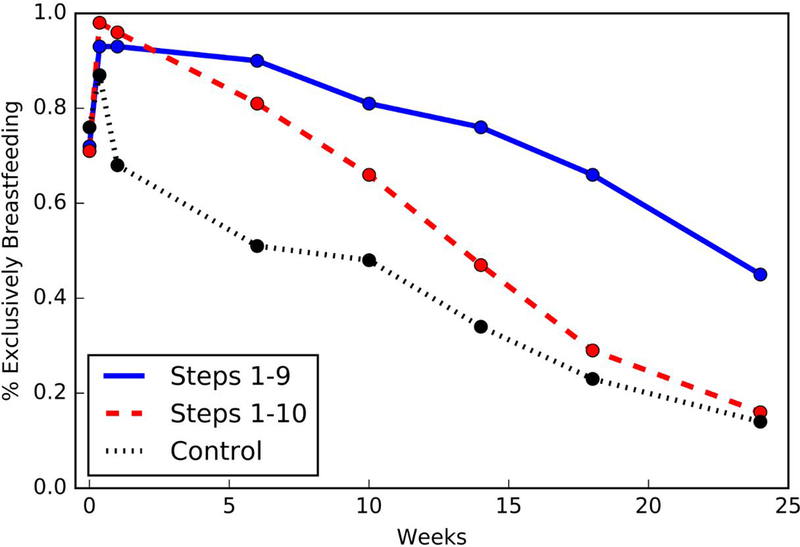
Prevalence of exclusive breastfeeding among mother-infant pairs between 0–24 weeks by clinic randomization. Exclusive breastfeeding was defined as breastfeeding with no additional fluid or food. Exclusive breastfeeding was assessed at 1 hour after birth, 2–3 days after birth, age 1, 6, 10, 14, 18, and 24 weeks. For Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI) steps 1–9, health-care staff from antenatal and maternity care (i.e. delivery rooms and post-partum wards) were trained using the WHO/UNICEF materials. For BHFI steps 1–10, health-care staff were trained using the WHO/UNICEF materials and additionally distributed flyers containing culturally appropriate messages developed to address the keys behaviors that were identified as main contributors to the sub-optimal breastfeeding practices in the pretrial survey to women and their families. Control clinics provided the standard of care.
