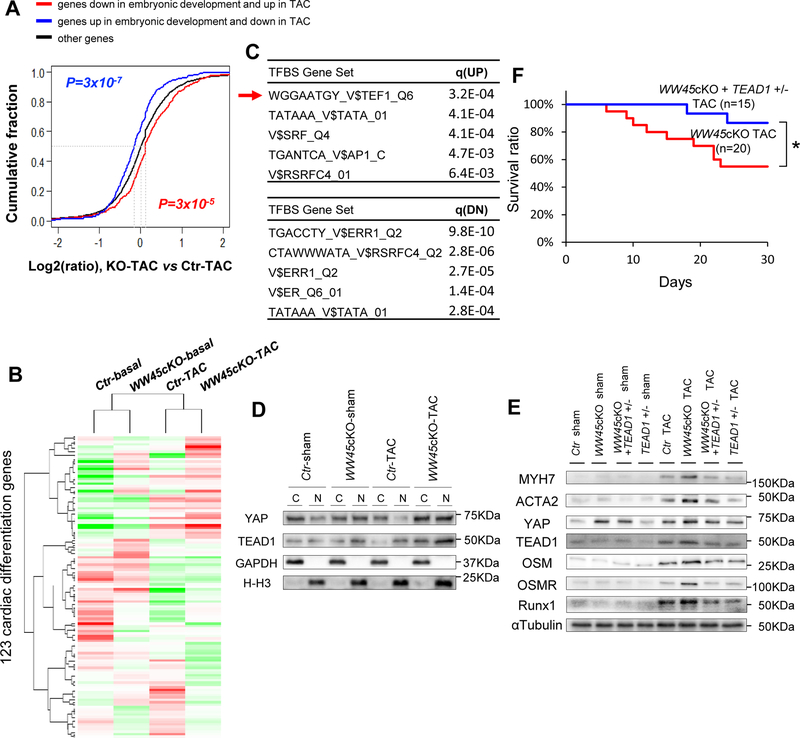
Figure 3: TEAD1 plays an essential role in mediating the exacerbation of heart failure in WW45 cKO mice in response to PO by facilitating CM de-differentiation.
(A) ECDF showing the difference in regulation between WW45cKO-TAC and Ctr-TAC for genes oppositely regulated in cardiac development and disease. Red line : genes DN in embryonic development and UP in TAC (n=438); Blue line : genes UP in embryonic development and DN in TAC (n=365); Black line : other genes. P-values are based on the K-S test comparing red or blue line genes with black line genes. (B) Heatmap showing relative expression of genes regarding cardiac differentiation. Gene set derived from the association of GO:0055007. The normalized read counts were subject to median centering before visualization. (C) TFBS analysis is based on UP or DN genes in WW45cKO vs Ctr (Arrow : TEAD1). Top five TFBS gene sets are shown with the q-values for false discovery rate control. (D) Representative gel pictures of immunoblot in the cytosolic and nuclear fractions of Ctr and WW45cKO mice 4 weeks after operation (n=4, each). (E) Representative gel pictures of immunoblot in the hearts of Ctr, WW45cKO, WW45cKO + TEAD1 +/− and TEAD1 +/− mice 4 weeks after operation. (F) Kaplan-Meier survival curves after TAC. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 by ANOVA. NS indicates not significant.