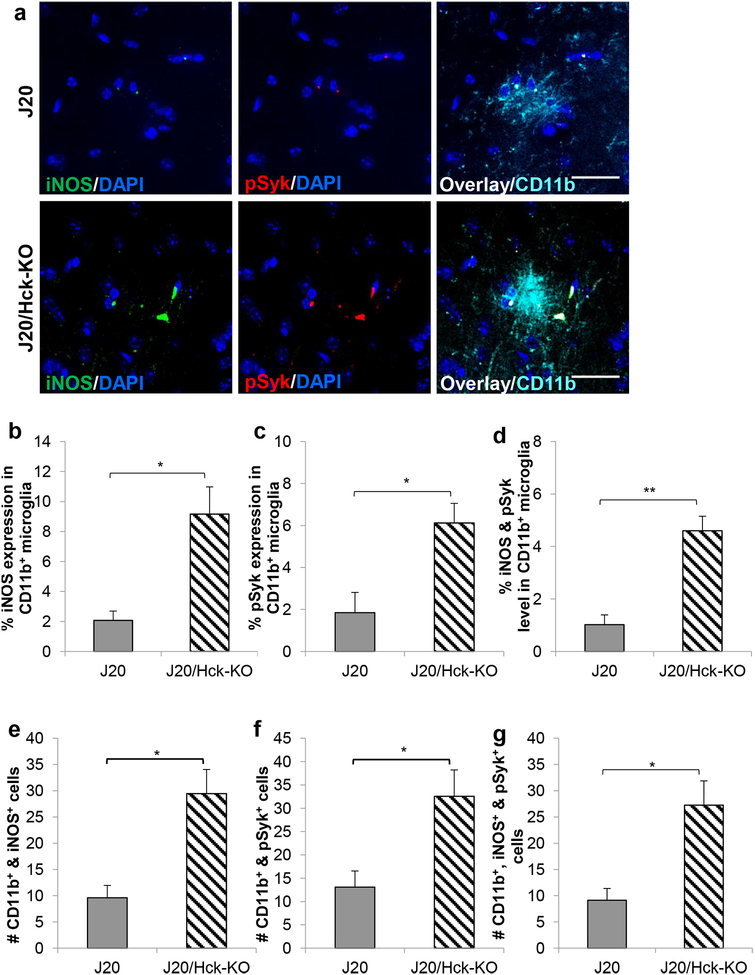
FIGURE 7.
Hck deficiency in J20 mice significantly elevated iNOS and pSyk expression in CD11b+ microglial clusters. (a) Representative images of iNOS (green) and pSyk (red) expressing in CD11b+ (cyan) microglial clusters in J20 (top) and J20/Hck-KO (bottom) mice (6–8 months old). Nuclei stained with DAPI were shown in blue. Scale bar, 20 μm. (b-d) Quantitative analyses of either % iNOS (b), pSyk (c), or both iNOS and pSyk (d) in the CD11b+ microglial clusters showed significantly higher expression in J20 mice depleted of Hck. (e-g) Clusters of microglial cells positively stained for CD11b and iNOS (e), CD11b and pSyk (f), as well as CD11b, iNOS and pSyk (g) were also counted. A significantly higher number of cells expressing either iNOS+, pSyk+ or iNOS+ and pSyk+ in CD11b+ cells were observed in J20 mice lacking Hck. Microglial clusters were analyzed in the hemibrains of 4–6 J20 (n = 12–15) and 4–5 J20/Hck-KO mice (n = 8–17). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from 1–2 sections per mouse. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 relative to J20 mice.