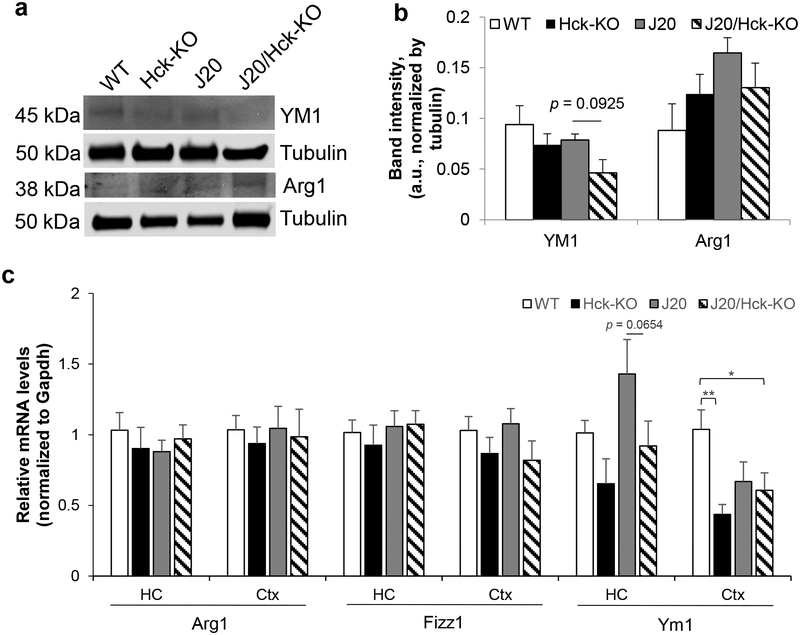
FIGURE 8.
Deleting Hck moderately reduced steady-state and mRNA levels of Ym1 in J20 mice. (a, b) Protein extracts from hippocampal tissues of 6–8 months old WT, Hck-KO, J20 and J20/Hck-KO mice were analyzed by Western blotting. (a) Representative immunoblots of microglial phagocytic markers, YM1 and Arg1, were shown. Tubulin was probed as loading control. (b) Quantitative analysis of YM1 and Arg1 band intensities after normalized to that of tubulin did not show significant differences between genotypes, but there was trend of lower YM1 protein levels in J20/Hck-KO mice as compared to J20 mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from n = 6–8 per genotype. (c) Relative expression of Arg1, Fizz1 and Ym1 mRNA levels were quantified by real-time PCR analyses from the hippocampus (HC) and cortex (Ctx) of WT, Hck-KO, J20 and J20/Hck-KO mice of 6–8 months old. mRNA level of Ym1 was reduced almost significantly (p = 0.0654) in the hippocampi of J20/Hck-KO mice as compared to J20 mice. However, significant reduction of Ym1 mRNA level was observed in the cortices of J20/Hck-KO mice as compared to WT mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from n = 3–5 hippocampi and n = 5–8 cortices per genotype. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 between indicated genotypes.