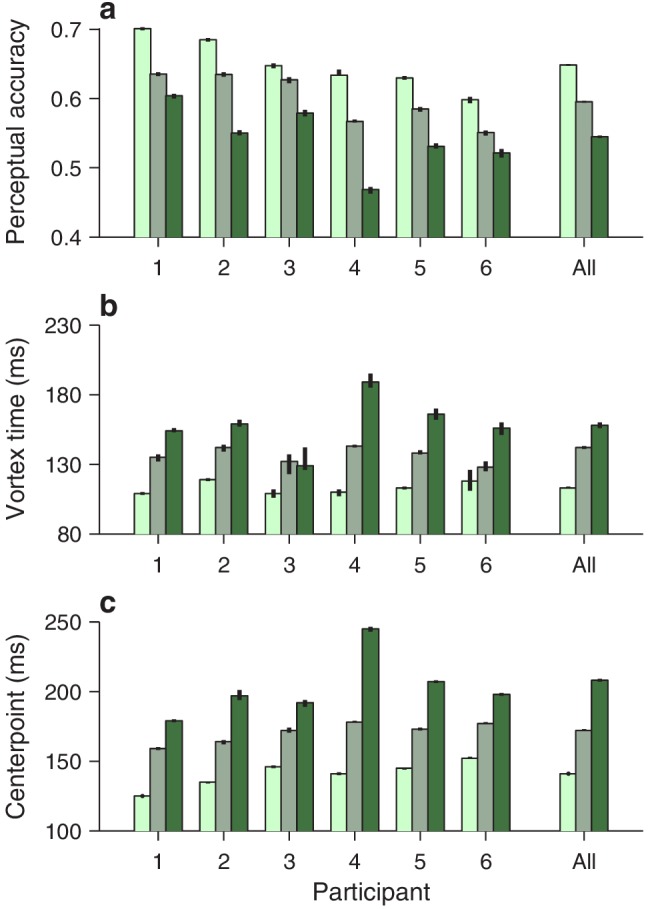
Figure 4. Perceptual performance quantified across participants and luminance conditions.
Each panel shows one particular quantity derived from the fitted tachometric curves, with results sorted by participant (x axes) and luminance level, high (bright green), medium (grayish green), and low (dark green). Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals obtained by bootstrapping. (a) Mean perceptual accuracy, calculated as the average value of the fitted tachometric curve for rPTs between 0 and 250 ms. (b) Vortex time, calculated as the rPT at which the minimum of the fitted tachometric curve is found. (c) Endogenous response centerpoint, equal to the rPT at which the rise of the fitted tachometric curve is halfway between its minimum and maximum values.
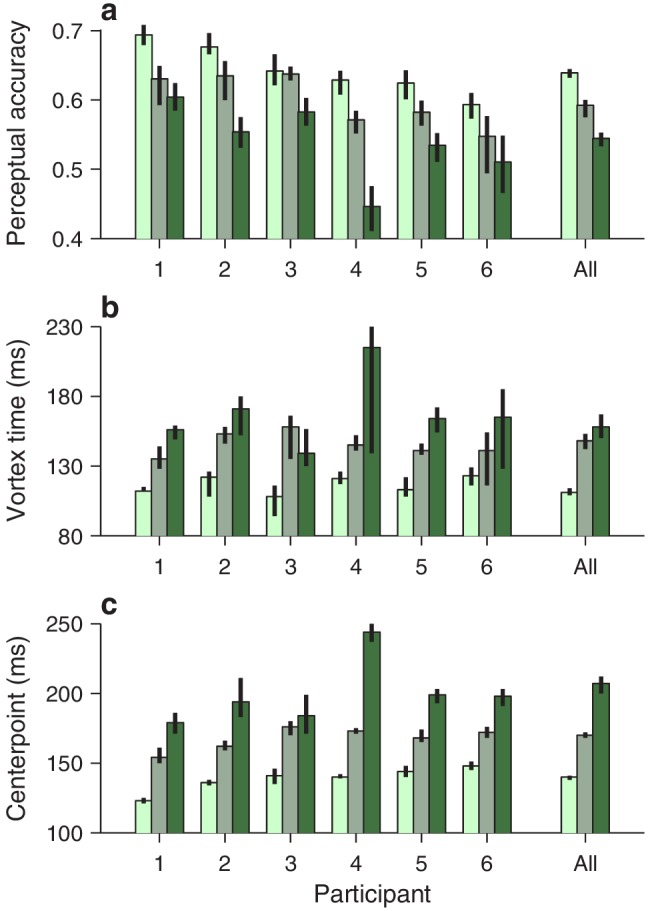
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Additional quantities that characterize perceptual performance across participants and cue conditions.
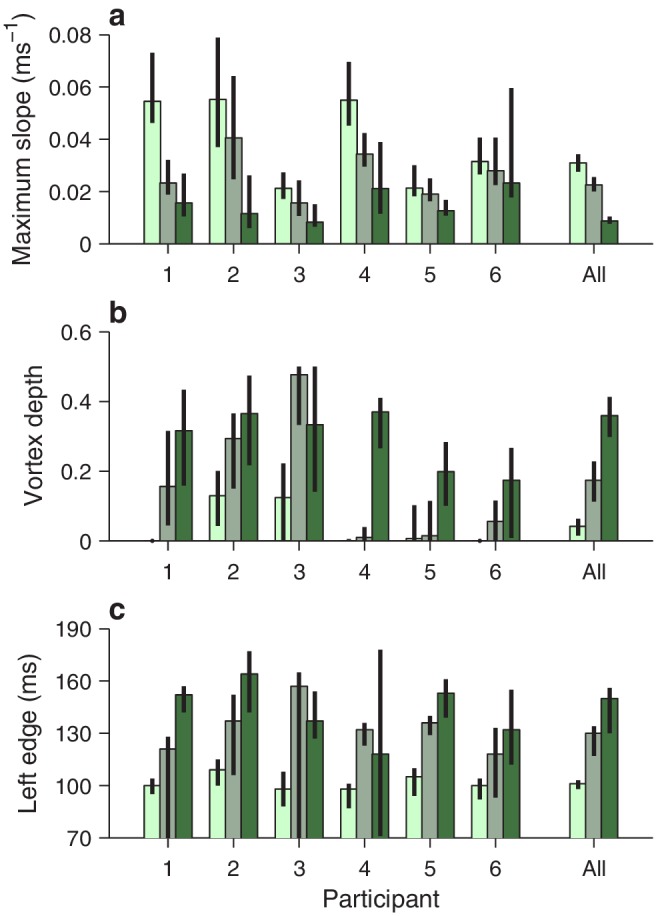
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Simulated perceptual performance quantified in the same way as the experimental data.