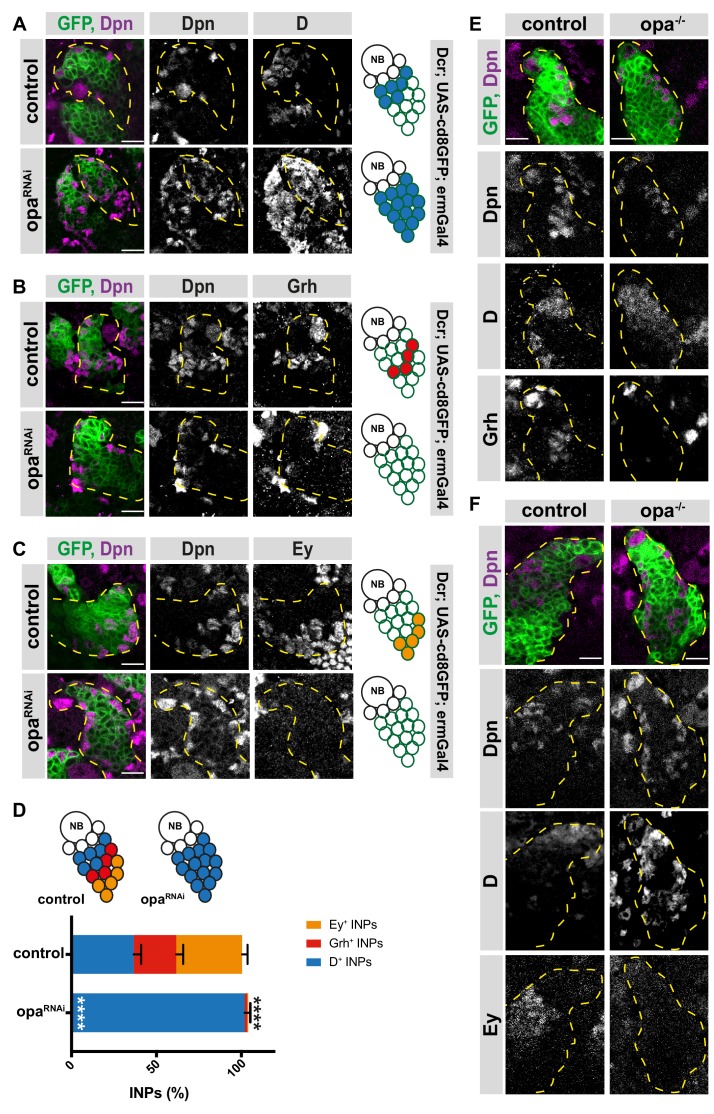
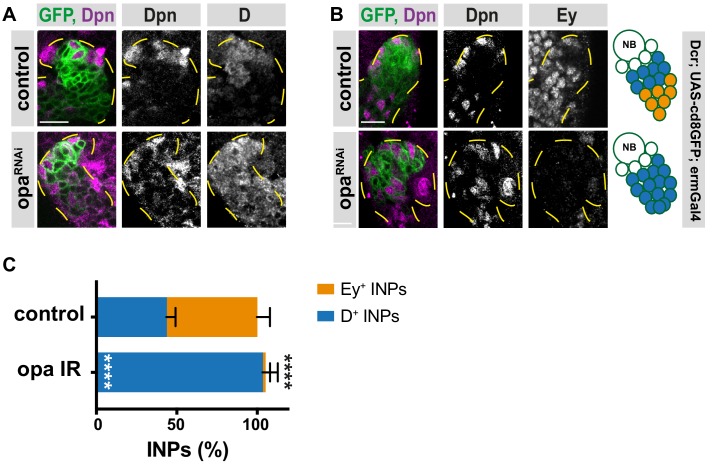
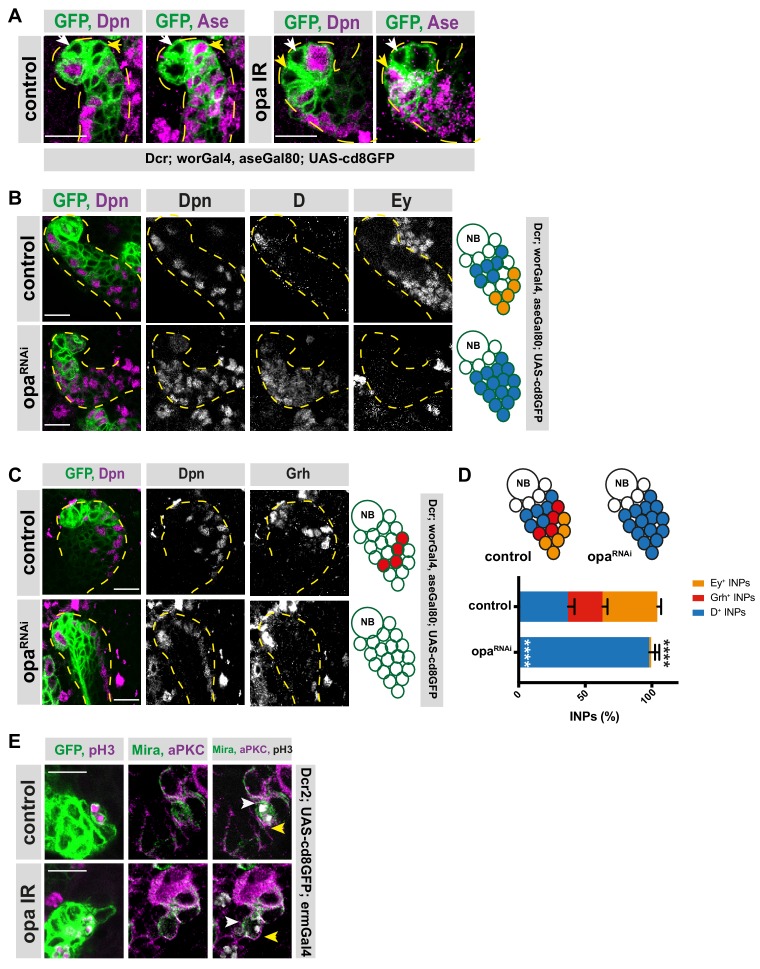
Figure 2. Opa is required for the progression of temporal patterning of INPs.
(A) Close-up images of larval brains expressing RNAi against opa in INPs, stained for Dpn and D (induced with ermGal4, marked with membrane bound GFP). Lineages are outlined with yellow dashed line. (B) Close-up images of larval brains expressing RNAi against opa in INPs, stained for Dpn and Grh (induced with ermGal4, marked with membrane bound GFP). Lineages are outlined with yellow dashed line. (C) Close-up images of larval brains expressing RNAi against opa in INPs, stained for Dpn and Ey (induced with ermGal4, marked with membrane bound GFP). Lineages are outlined with yellow dashed line. (D) Quantification of INP numbers in different temporal stages identified by antibody staining of Dpn+, D+ cells, Dpn+, Grh+ cells, and Dpn+, Ey+ cells in control and opa knock-down brains, n = 10, total INP numbers in control were normalized to 100%. Data represent mean ± SD, ***p<=0.001, Student’s t-test (D+ INPs control 12.44 ± 1.42 [n = 10], opa RNAi 34.66 ± 1.02 [n = 12], p<0.001; Grh+ INPs control 8.5 ± 1.32 [n = 10], opa RNAi 0.5 ± 0.65 [n = 12], p<0.001; Ey+ INPs control 13.2 ± 0.98 [n = 10], opa RNAi 0.2 ± 0.4 [n = 10], p<0.001). (E) Control and opa mutant MARCM clones marked by membrane-bound GFP, stained for Dpn, Grh and D after 120 hr of induction. Control clone has D+, Dpn+ INPs followed by Grh+ INPs while opa mutant clone has increased number of D+ INPs and decreased number of Grh+ INPs. (F) Control and opa mutant MARCM clones marked by membrane-bound GFP, stained for Dpn, D and Ey after 120 hr of induction. Opa mutant clone has higher number of D+ INPs and lower number of Ey+ INPs. Scale bar 10 μm in all images.