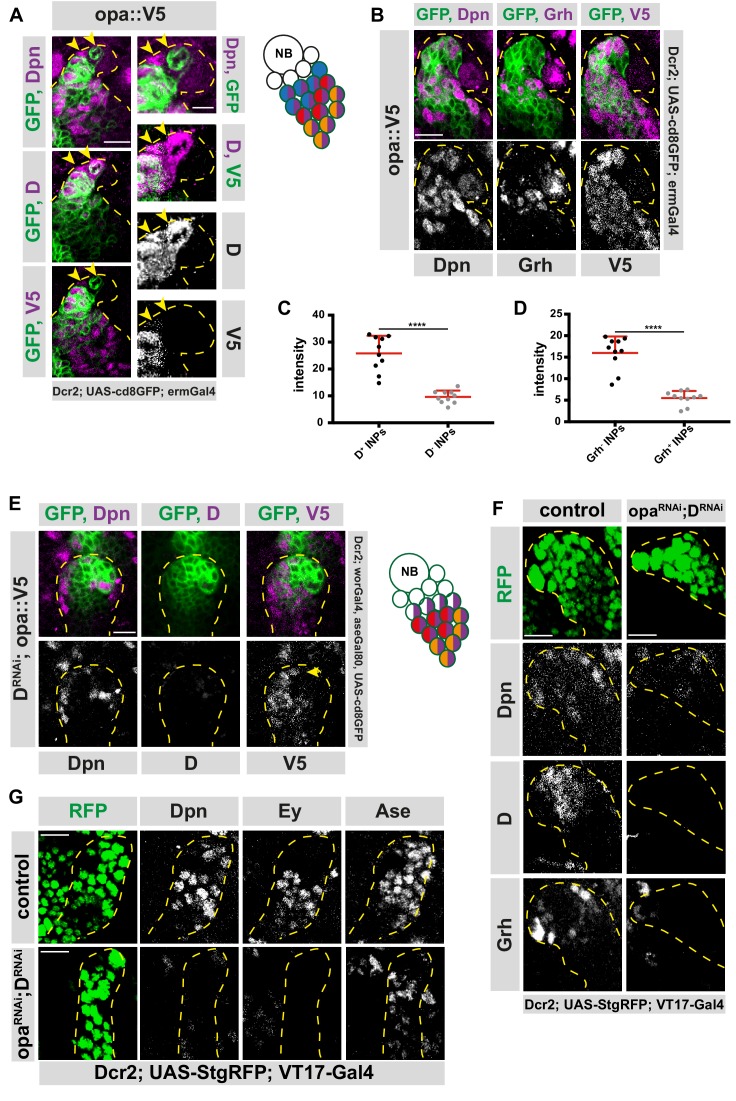
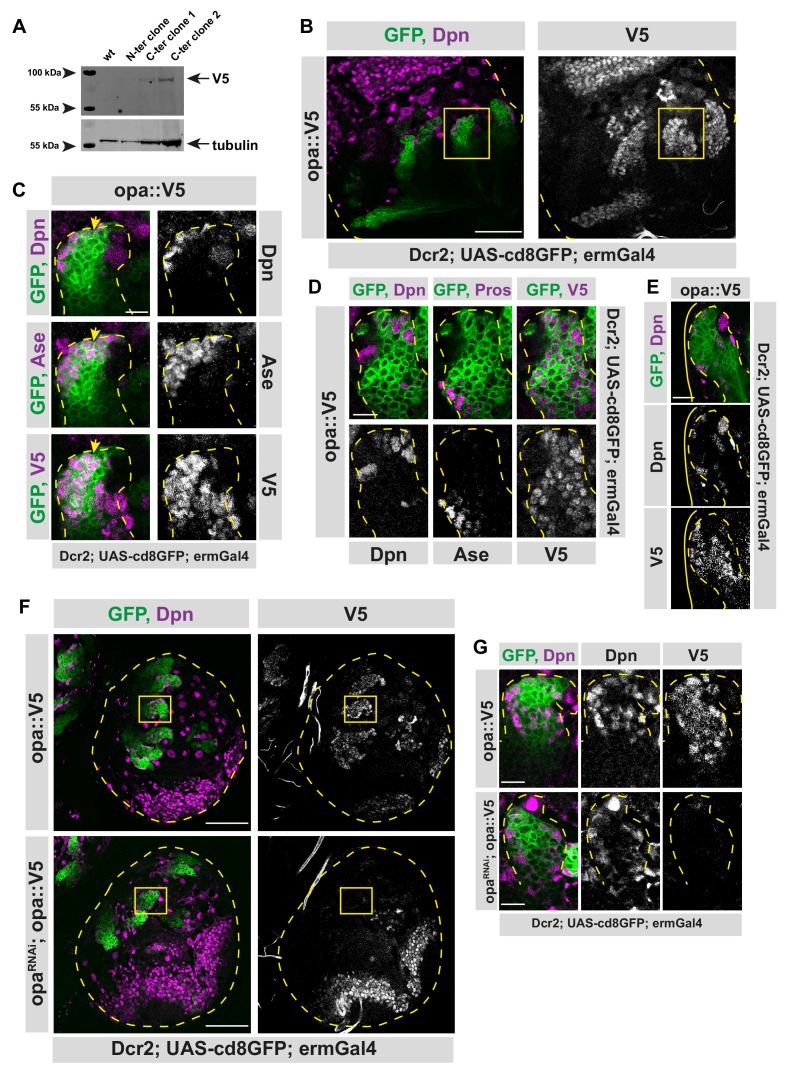
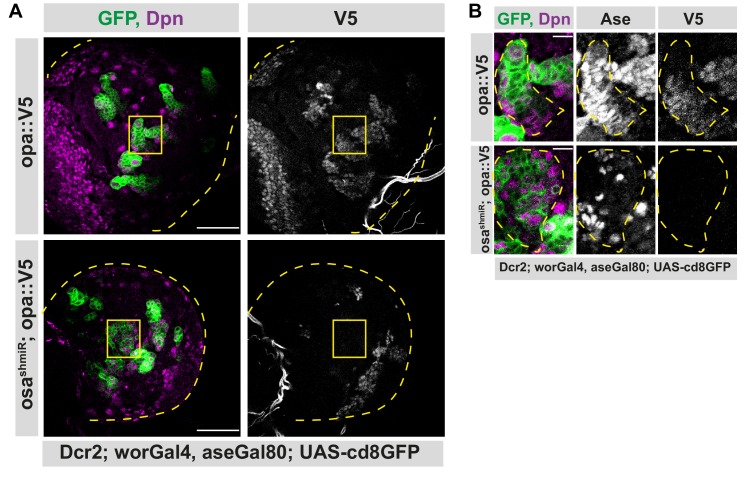
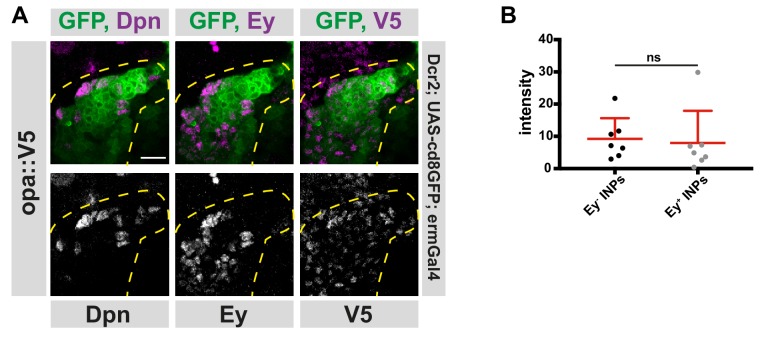
Figure 4. Osa initiates D expression before initiating Opa.
(A) Close-up images of fly brains endogenously expressing V5-tagged opa in INPs, stained for V5, Dpn and D. D+, V5- cell is marked with arrows, lineages are outlined with yellow dashed line, scale bar 10 μm and 5 μm, (induced with ermGal4, marked with membrane bound GFP). (B) Close-up images of fly brains endogenously expressing V5-tagged opa in INPs, stained for V5, Dpn and Grh, lineages are outlined with yellow dashed line, scale bar 10 μm, (induced with ermGal4, marked with membrane bound GFP). (C) Quantifications of opa::V5-signal intensity measurements of D+ vs D- INPs, n = 10, normalized to background intensity. Data represent mean ± SD, ***p<=0.001, Student’s t-test. (D) Quantifications of opa::V5-signal intensity measurements of Grh+ vs Grh- INPs, n = 10, normalized to background intensity. Data represent mean ± SD, ***p<=0.001, Student’s t-test. (E) Close-up images of fly brains endogenously expressing V5-tagged opa and RNAi for D in type II lineages, stained for V5, Dpn and D, lineages are outlined with yellow dashed line, scale bar 10 μm, (induced with worGal4, aseGal80, marked with membrane bound GFP). (F–G) Close up images of control versus opa and D double knock-down brains in type II lineages, stained with Dpn, D and Grh (C), or for Dpn, Ey and Ase (C) antibodies, lineages are outlined with yellow dashed lines, scale bar 10 μm, (induced with Dcr2; UAS-StgRFP; VT17-Gal4, marked with nuclear RFP).