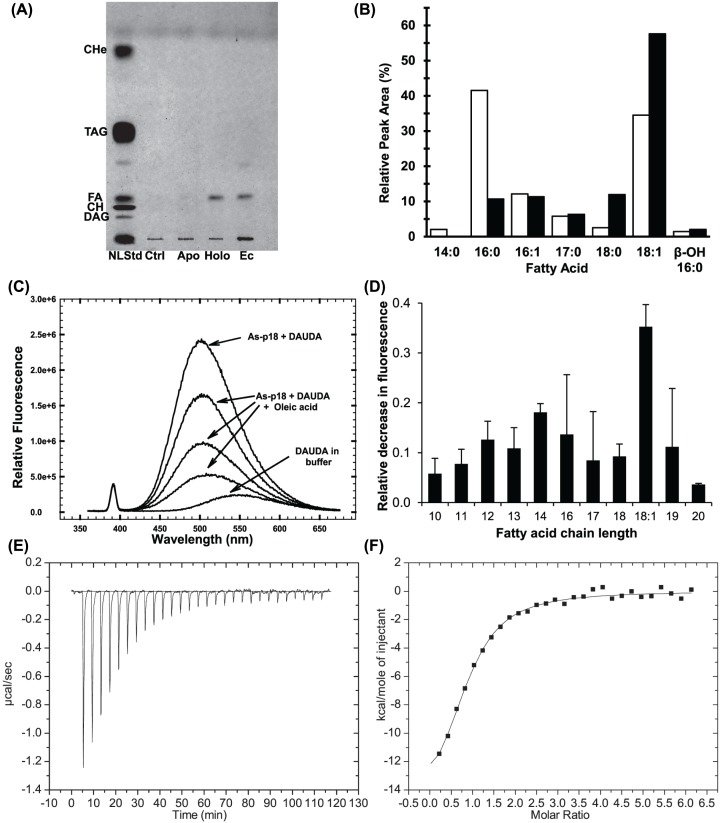
Figure 2. Ligand binding by As-p18.
(A) Thin layer chromatography of the lipids that co-purify with As-p18 under conditions that resolve fatty acids and neutral lipids. Holo and Apo, As-p18 purified without or with an HPLC step; NLStd, neutral lipid standard mixture from rat liver homogenate; Ctrl, buffer and solvents only; Ec, E. coli extract; CH, cholesterol; FA, free fatty acid; TAG, triacylglycerols; CHe, cholesterol ester. (B) Relative peak areas of the GC peaks of the methyl esters of the fatty acids that co-purify with As-p18 (filled bars) or that are present in E. coli extract (unfilled bars). (C) Fluorescence emission spectra (excitation at 345 nm) of 1 μM DAUDA in buffer or on the addition of 1.25 μM rAs-p18 and following the competitive displacement of DAUDA from rAs-p18 by the progressive addition of oleic acid: three additions of 10 μl of 1:100 dilution of a 10 mM stock solution of oleic acid were added directly to the fluorescence cuvette. (D) The relative decrease in fluorescence emission at 500 nm of the fatty acid analogue, DAUDA, upon displacement from As-p18 by fatty acids reveals the efficacy of 0.49 μM competing saturated or unsaturated (18:1) fatty acids. (E) Baseline corrected ITC data for the injection of 2% methyl-β-cyclodextrin-solubilized oleate into a solution of As-p18, and (F) the data plotted to show enthalpy per mole of oleate injected versus molar ratio and the fitted binding isotherm.