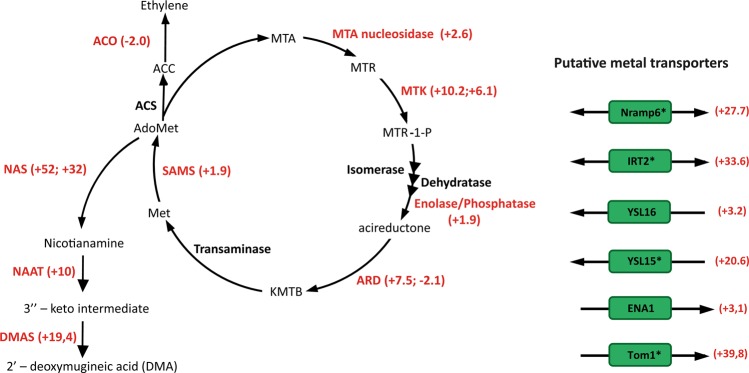
Figure 4.
Differentially expressed genes in rice roots following colonisation by H. seropedicae. Genes involved in siderophore synthesis and transport, the methionine salvage pathway and ethylene synthesis are shown. Numbers in parentheses represent the fold change. H. seropedicae SmR1 induces methionine recycling and mugineic acid (MA) synthesis as well as the expression of transporters involved in iron metabolism. The expression of those genes marked with an asterisk was confirmed by RT-qPCR Abbreviations: AdoMet, S-adenosylmethionine; ACC, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate; ACS, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase; ACO, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase; MTA, 5′-methylthioadenosine; MTR, 5′-methylthioribose; MTK, methylthioribose kinase; MTR-1-P, 5′-methylthioribose-1-phosphate; KMTB, 2-keto-4-methylthiobutyrate; ARD, acireductone dioxygenase; SAMS, S-adenosylmethionine synthetase; NAS, nicotianamine synthase; NAAT nicotianamine aminotransferase; DMAS, deoxymugineic acid synthase; Tom1, transporter of mugineic acid 1; ENA1 (efflux transporters of nicotianamine 1); Nramp6, Natural Resistance-Associated Macrophage Protein; IRT2(iron-regulated transporter 2); YSL16 (yellow strip-like gene 16); YSL15 (yellow strip-like gene 15).