Figure 1.
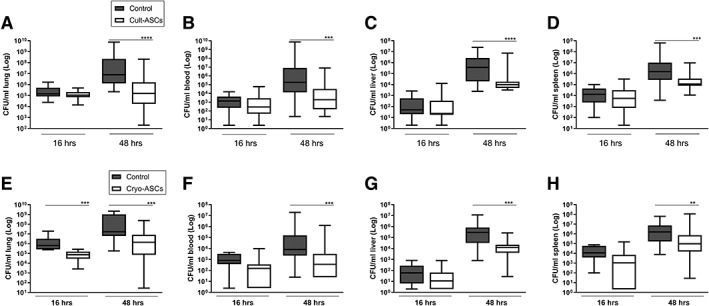
Infusion of cultured or cryopreserved adipose‐derived mesenchymal stem cells (ASCs) reduce bacterial burdens during pneumosepsis. Bacterial loads (colony‐forming units) in the lung, blood, liver, and spleen 16 and 48 hours after infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae via the airways in mice treated with 1 × 106 freshly cultured (Cult‐ASCs, A–D) or cryopreserved (Cryo‐ASCs, E–H) ASCs intravenously either 1 hour after bacterial inoculation (for measurements at 16 hours after infection) or 6 hours after infection (for measurements at 48 hours after infection). Data are expressed as box‐and‐whisker diagrams of eight mice per group at each time point, and a representative result of at least two (three for 48 hours) independent repeated experiments. **, p < .01; ***, p < .001; ****, p < .0001 versus the control group.
